Comparative analysis of small molecule and growth factor-derived human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells
- PMID: 40641603
- PMCID: PMC12240953
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1594340
Comparative analysis of small molecule and growth factor-derived human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells
Abstract
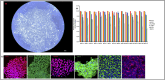
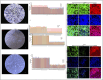
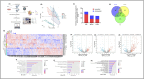
The growth factor and small molecule protocol are the two primary approaches for generating human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells (iPSC-HLCs). We compared the efficacy of the growth factor and small molecule protocols across fifteen different human iPSC lines. Morphological assessment, relative quantification of gene expression, protein expression and proteomic studies were carried out. HLCs derived from the growth factor protocol displayed mature hepatocyte morphological features including a raised, polygonal shape with well-defined refractile borders, granular cytoplasm with lipid droplets and/or vacuoles with multiple spherical nuclei or a large centrally located nucleus; significantly elevated hepatocyte gene and protein expression including AFP, HNF4A, ALBUMIN, and proteomic and metabolic features that are more aligned with a mature phenotype. HLCs derived from the small molecule protocol showed a dedifferentiated, proliferative phenotype that is more akin to liver tumor-derived cell lines. These experimental results suggest that HLCs derived from growth factors are better suited for studies of metabolism, biotransformation, and viral infection.
Keywords: growth factors; hepatocyte-like cells; hepatocytes; induced pluripotent stem cells; small molecules.
Copyright © 2025 Asumda, Alzoubi, Padarath, Jones, Kolhe, Mondal, Alptekin, Zhi, Lee, Huebert, Staff, Roberts and Kirkeby.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

