Efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of anxiety and depression in male sexual dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40641608
- PMCID: PMC12240729
- DOI: 10.1093/sexmed/qfaf048
Efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of anxiety and depression in male sexual dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Male Sexual Dysfunction (MSD), comprising erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PE), exhibits an age-related prevalence affecting 50% of males beyond their fourth decade. Beyond physiological manifestations, MSD with comorbid anxiety and depression exerts profound psychosocial impacts. Emerging evidence suggests Chinese Herbal Medicine (CHM) may offer therapeutic potential for addressing this clinical intersection.
Aim: To systematically assess the efficacy of CHM on alleviating anxiety and depression in patients with MSD via a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.
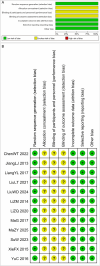
Methods: This study systematically searched four Chinese databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Database, China Biomedical Database, and VIP Database) and four international databases (PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library). Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating CHM interventions for MSD with comorbid anxiety and depression were identified.
Outcomes: The primary outcome focused on changes in symptoms of anxiety and depression, while secondary outcomes encompassed overall male sexual function improvement.
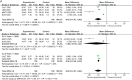
Results: By synthesizing data from 12 RCTs involving 1050 participants, our findings provide the first robust evidence that CHM significantly alleviates anxiety and depression in MSD, while concurrently improving core symptoms of MSD, such as PE and ED. Notably, CHM formulations demonstrated superior efficacy over SSRIs in improving both psychological scales, including Self-Rating Anxiety Scale [MD = -9.11, 95% CI (-11.53, -6.70), P < .05], Self-Rating Depression Scale [MD = -9.85, 95% CI (-14.07, -5.63), P < .05], the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) [MD = -5.30, 95% CI (-11.61, 1.01), P > .05], and the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale [MD = -3.89, 95% CI (-4.52,-3.27), P < .05], as well as MSD-specific metrics, such as International Index of Erectile Function-5 [MD = 3.26, 95% CI (1.98, 4.53), P < .05] and intravaginal ejaculation latency time [MD = 1.60, 95% CI (0.82, 2.37), P < .05]. Importantly, the lack of statistical significance in HAMD scores in our analysis may be attributed to the differences in treatment responses between the PE and ED populations.
Clinical implications: It provides evidence-based support to address the limitations of separating physical and mental symptoms in traditional treatment, further substantiates its application value within the integrated medical model, and explores new research avenues for designing personalized treatment plans for patients.
Strengths and limitations: A first-of-its-kind systematic evaluation was conducted to assess the comprehensive efficacy of traditional CHM in alleviating anxiety and depression symptoms while improving sexual function indicators among patients with MSD. The limited number of studies constitutes the most significant limitation.
Conclusions: Our findings provide the first robust evidence that CHM significantly alleviates anxiety and depression in MSD patients, while concurrently improving core MSD symptoms, such as PE and ED.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; anxiety; depression; male sexual dysfunction; psychosexual health; systematic review.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The International Society for Sexual Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no financial or personal conflicts that may have influenced the research presented in this article.
Figures



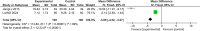


Similar articles
-
Psychosocial interventions for premature ejaculation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Aug 10;(8):CD008195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008195.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21833964
-
Pharmacotherapy for anxiety and comorbid alcohol use disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 20;1(1):CD007505. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007505.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25601826 Free PMC article.
-
[Chinese herbal medicine for side effects of transarterial chemoembolization in liver cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012 Dec;10(12):1341-62. doi: 10.3736/jcim20121204. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012. Retraction in: J Integr Med. 2013 Mar;11(2):151. PMID: 23257126 Retracted. Chinese.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for menopausal symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 15;3(3):CD009023. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009023.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26976671 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD006568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006568.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22592712
References
-
- Kupfer DJ, Regier DA, Narrow WE, et al. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. The United States: American Psychiatric Association; 2013, 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

