Characterization of bla NDM-5-carrying plasmids in two clinical Salmonella isolates from Jiaxing city, China
- PMID: 40641878
- PMCID: PMC12240926
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1620907
Characterization of bla NDM-5-carrying plasmids in two clinical Salmonella isolates from Jiaxing city, China
Abstract
Introduction: Salmonella is an important cause of foodborne diarrheal diseases worldwide. The emergence of bla NDM-positive carbapenem-resistant Salmonella enterica isolates in recent years poses a huge public health challenge.
Methods: In this study, two clinical S. enterica isolates carrying bla NDM-5: a serotype 4,[5],12:i:- strain (2023JX045) and a serovar Stanley strain (2024-406) were analyzed using antimicrobial susceptibility testing and whole genome sequencing.
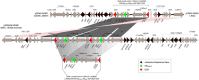
Results: Both isolates were multidrug resistant, with insusceptibility to ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cefuroxime, ceftiofur, cefazolin, cefoxitin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, cefepime, ceftazidime/avibactam, meropenem, imipenem, ertapenem, tetracycline, gentamicin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, florfenicol, chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, colistin, and polymixin B. The bla NDM-5-carrying plasmids in 2023JX045 and 2024-406 were named p23045-NDM5 and p2024406-NDM5, respectively, with both belonging to the incompatibility (Inc)HI2/IncHI2A group and sequence type ST3. In 2023JX045, bla NDM-5 was flanked by two same-oriented copies of IS26 elements (IS26-dsbC-trpF-ble MBL-bla NDM-5-IS5-ΔIS3000-ΔISKox3-umuC-umuD-IS26). In 2024-406, p2024406-NDM5 was found to carry two copies of bla NDM-5, possibly resulting from duplication of IS26-dsbC-trpF-ble MBL-bla NDM-5-IS5-ΔISAba125-ΔIS3000-ΔISKox3-umuC-umuD-IS26 and interrupted by mobile element IS1 at the upstream region of ΔIS3000.
Discussion: This is the first report to describe the presence of two bla NDM-5 copies on an IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmid carried by serovar Stanley, as well as the dissemination of bla NDM-5 in Salmonella in Jiaxing City, China. IS26-flanked composite transposons appeared to play an important role in the formation of this region. The dissemination of blaNDM in Salmonella isolates and the complexity of the bla NDM-5 region highlight the urgent need to monitor carbapenem-resistant S. enterica.
Keywords: IS26 unit; IncHI2/IncHI2A; blaNDM–5; carbapenem-resistant; non-typhoidal Salmonella.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Yuan, Yan, Jia, Gao, Liu, Sun, Zhu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment (2024). National foodborne disease surveillance manual in 2024. Beijing: China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

