Tissue-engineered tubular substitutions for urinary diversion in a preclinical rabbit model
- PMID: 40641968
- PMCID: PMC12241010
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1616977
Tissue-engineered tubular substitutions for urinary diversion in a preclinical rabbit model
Abstract
Objective: To develop and evaluate tissue-engineered tubular constructs using homologous adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs), smooth muscle cells (SMCs), and decellularized fish swim bladder (DFSB) matrix for urinary diversion in a rabbit model.
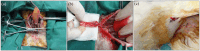
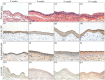
Methods: Rabbit ASCs and SMCs were isolated and expanded in vitro; cultured cells were seeded onto bilateral surfaces of DFSB scaffolds followed by 7-day incubation; cell-seeded matrices were shaped into tubular constructs; constructs underwent 2-week in vivo pre-vascularization within omental pouches. Experimental group rabbits (n=24) underwent complete bladder resection with replacement by pre-vascularized constructs, while control group (n=6) received identical implantation of acellular DFSB tubes. Histological evaluations were conducted at postoperative weeks 2, 4, 8, and 16; intravenous urography (IVU) was performed at 16-week endpoint.
Results: All experimental animals survived until scheduled sacrifice with histological evidence of: (1) luminal multilayer urothelium, (2) organized smooth muscle tissue on abluminal surfaces, and (3) construct-wide neovascularization of varying diameters; IVU confirmed absence of urinary leakage, stricture, or obstruction. Conversely, all control animals died within 2 weeks post-operation; autopsy revealed urine leakage, extensive scar formation, and severe inflammation as mortality causes.
Conclusion: Tissue-engineered tubular constructs fabricated from homologous ASCs, SMCs, and DFSB scaffold demonstrate feasibility as a viable urinary diversion alternative in rabbit models, showing functional tissue regeneration and superior outcomes versus acellular controls.
Keywords: adipose-derived stem cells; decellularized fish swim bladder; epithelium; smooth muscle cells; tissue engineering; urinary diversion.
Copyright © 2025 Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

