Hydrogen sulfide alleviates high-salt-stimulated myocardial fibrosis through inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- PMID: 40642013
- PMCID: PMC12240975
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1502269
Hydrogen sulfide alleviates high-salt-stimulated myocardial fibrosis through inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
Abstract
Background: Endogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and its key generating enzyme, cystathionine β-synthase (CBS), prevent vascular remodeling and damage to target organs during the advancement of hypertension induced by a high-salt diet.
Objective: The contribution of the H2S/CBS pathway to high-salt-induced myocardial fibrosis (MF) was explored, with a focus on the mechanistic involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α).
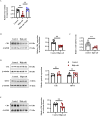
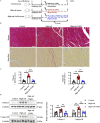
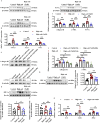
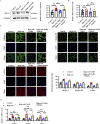
Methods: We used primary rat cardiac fibroblasts stimulated with high-salt medium and an MF model induced by a high-salt diet in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS), a commonly used H2S donor, was administered in vitro at 100 μmol/L and in vivo at 90 μmol/kg to maintain adequate H2S levels. An HIF-1α stabilizer, dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG), was used to maintain the HIF-1α protein level. The H2S/CBS pathway was followed using Western blotting and a sulfide-sensitive probe. The extent of MF was examined using histological and immunofluorescence staining techniques, including Sirius red and Masson trichrome. We performed Western blot analysis to measure fibrosis-related protein and HIF-1α protein levels.
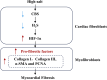
Results: High-salt exposure reduced H2S production and downregulated CBS protein expression in cardiac fibroblasts both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, the H2S donor inhibited the activation of cardiac fibroblasts triggered by high-salt conditions, while in vivo, it alleviated MF in salt-sensitive rats. From a mechanistic standpoint, high-salt exposure markedly upregulated HIF-1α expression. However, this increase was reversed by pretreatment with H2S. Furthermore, the HIF-1α stabilizer DMOG blocked the H2S-induced reduction in HIF-1α protein levels and consequently abolished the antifibrotic effect of H2S on cardiac fibroblasts exposed to high-salt conditions.
Conclusion: In conclusion, H2S attenuates high-salt-induced MF by suppressing fibroblast activity and collagen synthesis, potentially via downregulation of HIF-1α.
Keywords: HIF-1α; cardiac fibroblasts; high-salt diet; hydrogen sulfide; myocardial fibrosis.
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Huang, Lv, Tang, Jin and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats by inhibiting aerobic glycolysis-pyroptosis].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2025 Jun 25;77(3):465-471. doi: 10.13294/j.aps.2025.0015. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40566713 Chinese.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on expression in blood-brain barrier in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating HIF-1α/VEGF/MMP-9 signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jun 25;50(6):613-623. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20241047. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40551643 Chinese.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in Glioblastoma Multiforme: a systematic review going beyond pathologic implications.Oncol Res. 2024 Jul 17;32(8):1239-1256. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.052130. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39055895 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and its clinical significance in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Swiss Med Wkly. 2013 Sep 6;143:w13855. doi: 10.4414/smw.2013.13855. eCollection 2013. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013. PMID: 24018850
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

