A Rare Case Report of a Large Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxillary Sinus Associated With an Ectopic Maxillary Third Molar
- PMID: 40642023
- PMCID: PMC12245510
- DOI: 10.1155/crid/2436615
A Rare Case Report of a Large Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxillary Sinus Associated With an Ectopic Maxillary Third Molar
Abstract
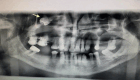
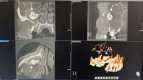
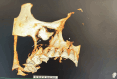
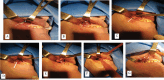
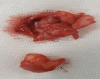
Ectopic eruption of permanent molars is an uncommon developmental anomaly characterized by abnormal tooth positioning, which can lead to significant complications. In rare instances, ectopic molars may be associated with dentigerous cysts, particularly within the maxillary sinus, posing challenges for diagnosis and management. This report discusses a rare case of a 58-year-old male who presented with chronic right maxillary sinusitis, intermittent facial pain, and purulent nasal and oral discharge. Radiological evaluation, including cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), revealed a completely opacified right maxillary sinus containing an ectopic maxillary molar. Additionally, a large cystic lesion consistent with a dentigerous cyst was found, occupying the entire sinus cavity. Surgical management was performed using the Caldwell-Luc approach under general anesthesia. This involved creating a bone window in the anterior maxillary wall to facilitate the removal of the ectopic tooth and the associated cystic lesion. Histopathological examination confirmed the presence of a dentigerous cyst exhibiting chronic inflammatory infiltration and fibrosis. Ectopic molars in the maxillary sinus are often asymptomatic but can present with recurrent sinusitis, pain, and oroantral communication. The existence of a large dentigerous cyst heightens the risk of complications and may obscure radiological interpretation due to sinus opacification. This case highlights the necessity of comprehensive imaging and early surgical intervention to prevent long-term complications. Awareness of such rare conditions can help clinicians in prompt diagnosis and appropriate management, ultimately preserving sinus function and minimizing further issues.
Keywords: Caldwell–Luc approach; cystic lesion; intrasinusal position of the molar; maxillary sinusitis; sinus opacification.
Copyright © 2025 Marika Ramishvili et al. Case Reports in Dentistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dentigerous Cyst Associated With Impacted Inverted Mesiodens: A Report of Three Cases and a Brief Literature Review.Case Rep Dent. 2025 Aug 3;2025:6989796. doi: 10.1155/crid/6989796. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Dent. 2025. PMID: 40786705 Free PMC article.
-
Impacted mandibular first molar with root encircling the inferior alveolar nerve and an odontogenic cyst formation.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):1022. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06400-9. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40604788 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of sinus lift procedures for dental implant rehabilitation: a Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010 Spring;3(1):7-26. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010. PMID: 20467595
-
Frequency of odontogenic lesions in patients with impacted maxillary canines and the association with impaction characteristics.Dent Med Probl. 2025 May-Jun;62(3):479-485. doi: 10.17219/dmp/165841. Dent Med Probl. 2025. PMID: 40644036
-
Surgical removal versus retention for the management of asymptomatic disease-free impacted wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 31;(8):CD003879. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003879.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 4;5:CD003879. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003879.pub5. PMID: 27578151 Updated.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

