Deep learning analysis of long COVID and vaccine impact in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs): development of a risk calculator in a multicentric study
- PMID: 40642241
- PMCID: PMC12240947
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1416273
Deep learning analysis of long COVID and vaccine impact in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs): development of a risk calculator in a multicentric study
Abstract
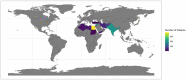
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a global pandemic affecting millions worldwide. This study aims to bridge the knowledge gap between acute and chronic symptoms, vaccination impact, and associated factors in patients across different low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Materials and methods: The study included 2,445 participants aged 18 years and older, testing positive for COVID-19. Data collection involved screening for medical histories, testing records, symptomatology, and persistent symptoms. Validated instruments, including the DePaul Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ-2) and the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), were used. We applied a self-supervised and unsupervised deep neural network to extract features from the questionnaire. Gradient boosted machines (GBM) model was used to build a risk calculator for chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), depression, and prolonged COVID-19 symptoms.
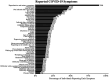
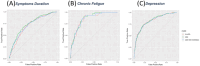
Results: Out of the study cohort, 68.1% of the patients had symptoms lasting longer than 2 weeks. The most frequent symptoms were loss of smell (46.8%), dry cough (40.1%), loss of taste (37.8%), headaches (37.2%), and sore throat (28.9%). The patients also reported high rates of depression (47.7%), chronic fatigue (6.5%), and infection after vaccination (23.7%). Factors associated with CFS included sex, age, and smoking. Vaccinated individuals demonstrated lower odds of experiencing prolonged COVID-19 symptoms, CFS, and depression. The predictive models achieved a high area under the curve (AUC) scores of 0.87, 0.82, and 0.74, respectively.
Conclusion: The findings underscore the significant burden of long-term symptoms such as chronic fatigue and depression, affecting a considerable proportion of individuals post-infection. Moreover, the study reveals promising insights into the potential benefits of vaccination in mitigating the risk of prolonged COVID-19 symptoms, CFS, and depression. Overall, this research contributes valuable knowledge towards comprehensive management and prevention efforts amidst the ongoing global pandemic.
Clinical trial registration: Clinical trials.gov, NCT05059184.
Keywords: COVID-19; LMICs; chronic fatigue syndrome; depression; hospitalization; long COVID; post-acute sequelae; vaccination.
Copyright © 2025 Shaheen, Shaheen, Long COVID Collaboration Study Group in the LMICs, Shoib, Saeed, Buhari, Bharmauria and Flouty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world impact of COVID-19 vaccination, household exposure, and circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants on infection risk and symptom presentation in a U.S./Mexico border community.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 9;13:1497390. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1497390. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40552239 Free PMC article.
-
Sero-prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Ethiopia: Results of the National Population Based Survey, 2021.PLoS One. 2025 May 6;20(5):e0313791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313791. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40327714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bull-Otterson L, Baca S, Saydah S, Boehmer TK, Adjei S, Gray S, et al. Post–COVID conditions among adult COVID-19 survivors aged 18–64 and ≥65 years — United States, march 2020–November 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2022) 71:713–7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7121e1 - DOI
-
- Ayoubkhani D, Bosworth ML, King S, Pouwels KB, Glickman M, Nafilyan V, et al. Risk of long COVID in people infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 after 2 doses of a coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine: community-based, matched cohort study. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2022) 9:ofac464. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac464, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

