An optimization method for hemi-diaphragm measurement of dynamic chest X-ray radiography during respiration based on graphics and diaphragm motion consistency criterion
- PMID: 40642297
- PMCID: PMC12241069
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1528067
An optimization method for hemi-diaphragm measurement of dynamic chest X-ray radiography during respiration based on graphics and diaphragm motion consistency criterion
Abstract
Introduction: Existing technologies are at risk of abnormal hemi-diaphragm measurement due to their abnormal morphology caused by lung field deformation during quiet breathing (free respiration or respiratory) interventions in dynamic chest radiography (DCR). To address this issue, an optimization method for hemi-diaphragm measurement is proposed, utilizing graphics and the consistency criterion for diaphragm motion.
Methods: First, Initial hemi-diaphragms are detected based on lung field mask edges of dynamic chest X-ray images abstracted from the DCR at respiratory interventions controlled by the radiologist's instructions. Second, abnormal hemi-diaphragms are identified, resulting from morphological deformation of the lung field during respiration. Lastly, these abnormal hemi-diaphragms are optimized based on the consistency criterion of diaphragm motion.
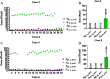
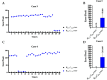
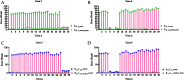
Results: Results show that the proposed optimization method can effectively measure the hemi-diaphragm, even in the presence of the inapparent cardiophrenic angle caused by abnormal deformations of the lung field morphology during respiration, reducing the mean error by 49.050 pixels (49.050 × 417 μm = 20,453.85 μm).
Discussion: Therefore, the proposed optimization method may become an effective tool for precision healthcare to find the pattern of diaphragm movement during respiratory interventions.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; diaphragm motion consistency criterion; dynamic chest radiography; graphics; hemi-diaphragm measurement; respiration.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Zheng, Guo, Wu, Gao, Li, Liu, Liu, Guo and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors YY, JZ, PG, TW, and YL were employed by Shenzhen Lanmage Medical Technology Co., Ltd. Author QG was employed by Neusoft Medical System Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Al-qaness M. A. A., Zhu J., Al-Alimi D., Dahou A., Alsamhi S. H., Abd Elaziz M., et al. (2024). Chest X-ray images for lung disease detection using deep learning techniques: a comprehensive survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 31, 3267–3301. 10.1007/s11831-024-10081-y - DOI
-
- Amin S. U., Taj S., Hussain A., Seo S. (2024). An automated chest X-ray analysis for COVID-19, tuberculosis, and pneumonia employing ensemble learning approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 87, 105408. 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105408 - DOI
-
- Arias-Martínez P., Lafranca P. P. G., Mohamed Hoesein F. A. A., Vincken K., Schlösser T. P. C. (2025). Techniques for respiratory motion-resolved magnetic resonance imaging of the chest in children with spinal or chest deformities: a comprehensive overview. JCM 14, 2916. 10.3390/jcm14092916 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

