The Toxicity of Dimethyl Sulfoxide Combined with the Alkylating Agent MNU on Mice: Focusing on Mortality and Activity Impairment
- PMID: 40642425
- PMCID: PMC12241661
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S521506
The Toxicity of Dimethyl Sulfoxide Combined with the Alkylating Agent MNU on Mice: Focusing on Mortality and Activity Impairment
Abstract
Objective: Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is known to enhance the absorption of chemicals. This study investigated the effects of DMSO in combination with the alkylating agent, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU), on the activity and mortality of mice, providing foundational data for solvent mixture use and health impact assessment.
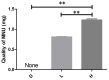
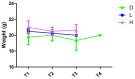
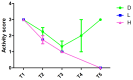
Methods: Twelve male SPF C57BL/6J mice were divided into three groups (n=4): DMSO group (D), DMSO combined with low-dose (L), and high-dose MNU group (H). Mice in D received intraperitoneal injections of pure DMSO solution at 12 mL/kg. The L or D group was injected with a DMSO solution containing 40 mg/kg or 60 mg/kg MNU at 12 mL/kg, respectively. Mice were monitored for changes in body weight, activity levels (walking, body stretching, fur condition), and mortality at various time points.
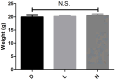
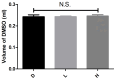
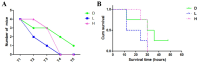
Results: Pre-injection, all groups showed no statistical differences in weight or DMSO dose, while the MNU injection dose was significantly different (H>L>D). Within 2 hours post-injection, all mice except one in the D group exhibited reduced mobility, hunched posture, and lethargy. Mortality progressed rapidly, with one D and two L mice dying by 12 hours, followed by additional deaths (one D, two L, and two H mice) at 24 hours. By 36 hours, all mice in L and H groups had died, while one D mouse recovered normal activity. At the 48-hour endpoint, only one D mouse survived with normal behavior. No significant differences in weight, activity levels and mortality changes were observed in surviving mice throughout the study period.
Conclusion: DMSO has certain toxicity, and when combined with alkylating agents such as MNU, it can lead to reduced activity and an increased mortality rate in mice. It is recommended to closely monitor the mice during the use of such reagents and to establish appropriate research observation protocols.
Keywords: MNU; dimethyl sulfoxide; mice; mortality; physiological effects; toxicity.
© 2025 Yan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest regarding the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

