Early-life adversities compromise behavioral development in male and female mice heterozygous for CNTNAP2
- PMID: 40642450
- PMCID: PMC12245450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2025.100726
Early-life adversities compromise behavioral development in male and female mice heterozygous for CNTNAP2
Abstract
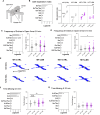
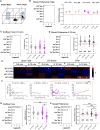
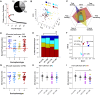
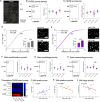
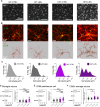
The etiological complexity of psychiatric disorders arises from the dynamic interplay between genetic and environmental vulnerabilities. Among the environmental components, early-life adversities are a major risk factor for developing a psychiatric condition. Yet, the interaction between adversities early in life and genetic vulnerability contributing to psychopathology is poorly understood. To fill this gap, we took advantage of the ideally controlled conditions of a pre-clinical approach. We raised a mouse model with genetic predisposition for multiple psychiatric disorders (autism spectrum, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder), the Cntnap2 +/- mouse, with limited bedding and nesting (LBN), a well-established paradigm to induce early-life stress in rodents. These mice were compared to LBN-raised Cntnap2 +/+ littermates, as well as parallel groups of Cntnap2 +/+ and Cntnap2 +/- raised in standard conditions. Using a battery for behavioral phenotyping we show that early-life adverse experience shapes non-overlapping phenotypic landscapes based on genetic predisposition. Specifically, LBN-raised Cntnap2 +/- mice displayed a perseverative risk-taking behavior in the elevated plus maze. Interestingly, this trait was highly predictive of their success in social interaction, suggesting that the intrusion of anxiety into the social behavioral domain may contribute to extreme gain- or loss-of function in sociability. Finally, we show that LBN promotes hypertrophy of post-synaptic densities in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala (BLA), but only in Cntnap2 +/- raised in LBN this is associated with microglia abnormalities. We conclude that the interplay between early-life adversities and Cntnap2 haploinsufficiency alters emotion regulation in mice, putatively as a consequence of deficient synaptic scaling in the BLA.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Publishing; Washington, DC, USA: 2022. Text Revision (DSM-5-TR), ISBN 978-0-89042-575-6.
-
- Bagheri F., Goudarzi I., Lashkarbolouki T., Elahdadi Salmani M., Goudarzi A., Morley-Fletcher S. The combined effects of perinatal ethanol and early-life stress on cognition and risk-taking behavior through oxidative stress in rats. Neurotox. Res. 2022;40:925–940. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00506-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

