Effect of Empagliflozin on Cardiovascular Mortality and Heart Failure Hospitalizations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 40642671
- PMCID: PMC12241828
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.85669
Effect of Empagliflozin on Cardiovascular Mortality and Heart Failure Hospitalizations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
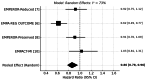
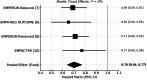
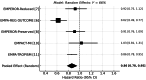
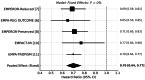
Empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, has demonstrated clinically meaningful benefits in patients with heart failure (HF). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effect of empagliflozin on cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization for heart failure (HHF) across randomized controlled trials (RCTs). A comprehensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Google Scholar, identifying five eligible RCTs. Studies were included if they evaluated empagliflozin's impact on cardiovascular mortality and HHF. A meta-analysis was performed using hazard ratios (HRs) for cardiovascular death and HHF. Data were synthesized using fixed- or random-effects models based on the degree of heterogeneity. The meta-analysis included 23,344 patients, of whom 12,849 received empagliflozin. Cardiovascular mortality was significantly reduced with empagliflozin (HR 0.86; 95% CI: 0.78-0.96). For HHF, empagliflozin reduced the risk by 30% (HR 0.70; 95% CI: 0.64-0.77) across all trials. Sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of these results. Empagliflozin significantly reduces cardiovascular mortality and HHF, supporting its use as a cornerstone therapy in heart failure management, especially in patients at high cardiovascular risk. These findings highlight the potential of empagliflozin as a key therapeutic intervention in heart failure care.
Keywords: cardiovascular mortality; empagliflozin; heart failure; heart failure hospitalizations; sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (sglt2) inhibitors.
Copyright © 2025, Rauf et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
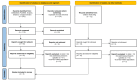
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
