Cross-border spread of a mosaic resistance (OXA-48) and virulence (aerobactin) plasmid in Klebsiella pneumoniae: a European Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Surveillance Network investigation, Europe, February 2019 to October 2024
- PMID: 40642770
- PMCID: PMC12262110
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.27.2500439
Cross-border spread of a mosaic resistance (OXA-48) and virulence (aerobactin) plasmid in Klebsiella pneumoniae: a European Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Surveillance Network investigation, Europe, February 2019 to October 2024
Erratum in
-
Authors' correction for Euro Surveill. 2025;30(27).Euro Surveill. 2025 Nov;30(47):251127c. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.47.251127c. Euro Surveill. 2025. PMID: 41287542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
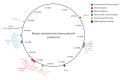
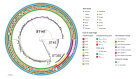
An investigation of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Surveillance Network (EURGen-Net) detected the same mosaic IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR) resistance (OXA-48) and virulence (aerobactin) plasmid in 492 Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from eight European Union countries during 2019-2024. Involvement of various K. pneumoniae sequence types (STs), multiple introductions, followed by large clonal outbreaks of three STs (ST147, ST392, ST45) carrying the plasmid in two countries indicate a high risk for further spread of this plasmid and a potential for difficult-to-treat K. pneumoniae infections to rise.
Keywords: Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales; antimicrobial resistance; cross-border spread; surveillance; virulence; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
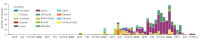
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). ECDC study protocol for genomic-based surveillance of carbapenem-resistant and/or colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae at the EU level - version 2.0. Stockholm: ECDC; 2018. Available from: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/ecdc-study-protocol-genomic-...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
