Nature-Inspired Compounds Targeting Escherichia coli WrbA as Biofilm-Modulating Agents: Computational Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation
- PMID: 40643025
- PMCID: PMC12247152
- DOI: 10.1002/ardp.70049
Nature-Inspired Compounds Targeting Escherichia coli WrbA as Biofilm-Modulating Agents: Computational Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation
Abstract
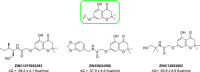
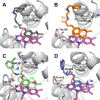
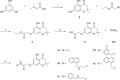
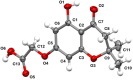
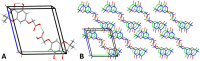
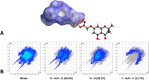
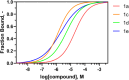
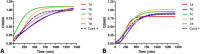
Biofilms pose significant challenges in multiple settings due to their resistance to conventional treatments. In this study, we designed and synthesized a novel class of nature-inspired 5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethylchroman-4-one derivatives as binders of WrbA, a potential target for biofilm modulation. Using a structure-based computational approach, a small library of analogs with varied amide moieties was developed and synthesized. The evaluation of their binding affinity to WrbA demonstrated good-to-excellent Kd values, as confirmed by microscale thermophoresis (MST). Antibiofilm assays against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus revealed different modulating effects on biofilm formation, conceivably linked to ROS production. These findings emphasize the importance of ROS levels in biofilm, as well as the pivotal role of WrbA as a target in its regulation.
Keywords: MM‐GBSA; antibiofilm assay; chroman‐4‐one derivatives; microscale thermophoresis; reactive oxygen species.
© 2025 The Author(s). Archiv der Pharmazie published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of Deutsche Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ciofu O., Moser C., Jensen P. Ø., and Høiby N., “Tolerance and Resistance of Microbial Biofilms,” Nature Reviews Microbiology 20 (2022): 621–635. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

