Depression among married female adolescents in Bangladesh: the toll of marriage, pregnancy, and violence
- PMID: 40643167
- PMCID: PMC12247659
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.15.04033
Depression among married female adolescents in Bangladesh: the toll of marriage, pregnancy, and violence
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a critical psychiatric condition that is spreading faster among adolescents than adults around the globe. In low and middle-income countries, married female adolescents are more vulnerable to MDD than unmarried female adolescents. We aimed to estimate the prevalence of MDD among currently married female adolescents (CMFAs) in Bangladesh and determine its association with sociodemographic factors, factors related to marriage and childbearing, and social safety.
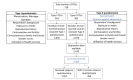
Methods: We used data from the Bangladesh Adolescent Health and Well-being Survey (BAHWS) 2019-20, the first national-level survey conducted on adolescents ages 15-19 in Bangladesh. The BAHWS 2019-20 included a total of 2408 CMFAs aged 15-19 years and collected depression data using the modified Indian Bangla version of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), which is specific to adolescents. We used multivariable logistic regression and Poisson regression with robust variance to examine the factors associated with MDD.
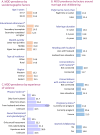
Results: The estimated prevalence of MDD among CMFAs aged 15-19 years is 14.6%. The odds of MDD did not vary by age, education, wealth, residence type, or region. The CMFAs who felt connected with their husband and mother-in-law were 31% (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) = 0.69; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.53-0.91) and 34% (aOR = 0.66; 95% CI = 0.47-0.92) less likely to have MDD than the rest, respectively. The odds of MDD were almost 2-fold (aOR = 1.77; 95% CI = 1.24-2.52) among pregnant CMFAs than their non-pregnant counterparts. We found significantly higher odds of MDD among CMFAs who experienced physical violence from their husbands (aOR = 1.93; 95% CI = 1.31-2.85) or others (aOR = 2.07; 95% CI = 1.15-3.71), any form of sexual harassment (aOR = 2.25-95% CI = 1.49-3.42), and cyberbullying (aOR = 3.73; 95% CI = 2.01-6.93) than those who did not experience such adverse events.
Conclusions: We observed a high prevalence of MDD among CMFAs, without clustering in any specific sociodemographic group. It is associated with not feeling connected with husband and mother-in-law, having a health condition (pregnancy), and experiencing physical, sexual, and cyber abuse. Findings suggest integrating mental health programs in maternity care and preventing violence against women may help prevent and manage MDD.
Copyright © 2025 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest: The authors completed the ICMJE Disclosure of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author) and disclose the following activities and/or relationships: Shusmita Khan is currently working at USAID but she was not at USAID when the research for the current paper was conducted. The views and opinions expressed in this paper are those of the authors and not necessarily the views and opinions of the United States Agency for International Development.
Figures
References
-
- Joseph S, De Guzman R.Relationship between psychological well-being and depression among selected adolescents. Indian J Posit Psychol. 2021;12:232–5.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources