Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Prevents Aβ25-35-Induced Inflammation in Rats via Lipoxygenase Inhibition
- PMID: 40643478
- PMCID: PMC12249324
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14130957
Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Prevents Aβ25-35-Induced Inflammation in Rats via Lipoxygenase Inhibition
Abstract
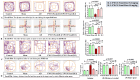
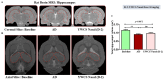
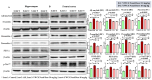
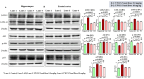
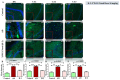
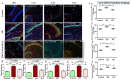
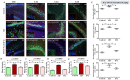
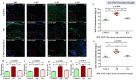
Neuroinflammation, triggered by lipoxygenase (LOX), contributes to Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression. Overexpression of LOX-5 in patients with AD serum highlights its role. This study assessed the efficacy of the LOX-inhibitor-peptide YWCS in an AD rat model induced by Aβ25-35 injection. Cognitive tests, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and molecular analyses were conducted. YWCS treatment significantly improved cognitive function, as evidenced by improved performance in the open field, novel object recognition, elevated plus maze, and Morris water maze tests. MRI scans revealed hippocampal shrinkage in AD rats and no changes were observed from YWCS treatment. Molecular analysis revealed altered expression of LOX-5, LOX-12, Aβ, γ-secretase components, p-Tau181, Akt, p-Akt, and p53 in AD rats. Immunofluorescence staining confirmed increased expression of LOX, Aβ, and p-Tau181 in the hippocampus of AD rats, which was reduced by YWCS treatment. Serum LOX levels were elevated in AD rats and significantly decreased after YWCS treatment, aligning with previous findings in human AD patients and AD cell models. YWCS offered improvements in behavioral and inflammatory marker regulation and also prevented progression of the disease, as shown by MRI results. These results suggest that YWCS, by targeting LOX, has the potential to be a promising therapeutic agent for AD.
Keywords: AD rat model; MRI scan; cognitive behavioral assessment; immunoblot; immunofluorescence; lipoxygenase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

