Immunotherapy for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer as a Glimmer of Hope
- PMID: 40643516
- PMCID: PMC12248509
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14130995
Immunotherapy for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer as a Glimmer of Hope
Abstract
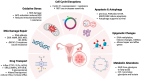
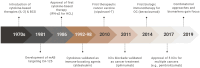
Ovarian cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, with platinum resistance posing a significant challenge. Conventional therapies often fail in these cases, highlighting the urgent need for novel treatment approaches. Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising strategy, offering renewed hope for patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer (PROC). This review explores the current landscape of immunotherapies for PROC, discussing different approaches, their mechanisms of action, and the potential for overcoming the limitations of conventional treatments.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; cell-based therapies; ovarian cancer; tumor microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jan Brancewicz was employed by the company Cellis AG. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Kempf E., Desamericq G., Vieites B., Diaz-Padilla I., Calvo E., Estevez P., Garcia-Arreza A., Martinez-Maestre M.A., Duran I. Clinical and Pathologic Features of Patients with Non-Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Retrospective Analysis of a Single Institution 15-Year Experience. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017;19:173–179. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1517-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical