The Level of Thiol-Oxidised Plasma Albumin Is Elevated Following a Race in Australian Thoroughbred Horses
- PMID: 40644475
- PMCID: PMC12249229
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70487
The Level of Thiol-Oxidised Plasma Albumin Is Elevated Following a Race in Australian Thoroughbred Horses
Abstract
Background: The extent to which muscle strain or tears are affecting race performance in horses is unknown because it is difficult to objectively identify muscle damage. One approach includes the use of physiological markers in blood. Recently, we linked the level of plasma thiol-oxidised albumin, an oxidative stress biomarker, to muscle damage in humans.
Objectives: This aim of this work was to investigate whether the level of plasma thiol-oxidised albumin was elevated in the days following a thoroughbred horse race.
Study design: 'In vivo' experiments.
Methods: Blood collection was performed by each trainer at their respective stable. Dried blood samples were collected for the level of thiol-oxidised albumin before and each day for 7 days post-race. Liquid blood samples were collected for analysis of the muscle enzymes creatine kinase (CK) and aspartate amino transferase (AST) before and on Day 2 and 5 post-race and were analysed by external pathology centre.
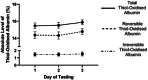
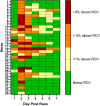
Results: The level of thiol-oxidised albumin peaked at 2 days post-race, increasing by 3.9 ± 0.7% (p < 0.0001) and returned to pre-race levels by Day 5. Thiol-oxidised albumin also correlated with the activity of AST (R2 = 0.2, p = 0.01). The time of recovery for thiol-oxidised albumin varied between individual horses, some recovered at Day 3 post-race whereas others extended beyond 7 days post-race.
Main limitations: No histological or imaging diagnosis was conducted to confirm that horses with elevated levels of thiol-oxidised albumin also had definitive evidence of muscle damage. The activity of CK and AST was not measured daily, as was the case for the level of thiol-oxidised albumin.
Conclusions: The level of thiol-oxidised albumin has the potential to be useful in managing recovery and return to training or competition in horse following a bout of damaging exercise, particularly given the ease of collecting small serial small blood samples.
Keywords: muscle damage; oxidative stress; physical exercise; thiol‐oxidised plasma albumin; thoroughbred horse; training.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Arslan, M. , Özcan M., Tosun C., Çötelioğlu Ü., and Matur E.. 2002. “The Effects of Physical Exercise on Some Plasma Enzymes and Ca and P Levels in Race Horses.” İstanbul Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi 28: 91–97.
-
- Bos, A. , Compagnie E., and Lindner A.. 2018. “Effect of Racing on Blood Variables in Standardbred Horses.” Veterinary Clinical Pathology 47: 625–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

