Allocating limited surveillance effort for outbreak detection of endemic foot and mouth disease
- PMID: 40644517
- PMCID: PMC12273912
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012395
Allocating limited surveillance effort for outbreak detection of endemic foot and mouth disease
Abstract
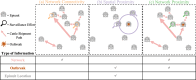
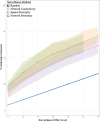
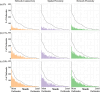
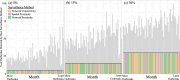
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) affects cloven-hoofed animals globally and has become a major economic burden for many countries around the world. Countries that have had recent FMD outbreaks are prohibited from exporting most meat products; this has major economic consequences for farmers in those countries, particularly farmers that experience outbreaks or are near outbreaks. Reducing the number of FMD outbreaks in countries where the disease is endemic is an important challenge that could drastically improve the livelihoods of millions of people. As a result, significant effort is expended on surveillance; but there is a concern that uninformative surveillance strategies may waste resources that could be better used on control management. Rapid detection through sentinel surveillance may be a useful tool to reduce the scale and burden of outbreaks. In this study, we use an extensive outbreak and cattle shipment network dataset from the Republic of Türkiye to retrospectively test three possible strategies for sentinel surveillance allocation in countries with endemic FMD and minimal existing FMD surveillance infrastructure that differ in their data requirements: ranging from low to high data needs, we allocate limited surveillance to [1] farms that frequently send and receive shipments of animals (Network Connectivity), [2] farms near other farms with past outbreaks (Spatial Proximity) and [3] farms that receive many shipments from other farms with past outbreaks (Network Proximity). We determine that all of these surveillance methods find a similar number of outbreaks - 2-4.5 times more outbreaks than were detected by surveying farms at random. On average across surveillance efforts, the Network Proximity and Network Connectivity methods each find a similar number of outbreaks and the Spatial Proximity method always finds the fewest outbreaks. Since the Network Proximity method does not outperform the other methods, these results indicate that incorporating both cattle shipment data and outbreak data provides only marginal benefit over the less data-intensive surveillance allocation methods for this objective. We also find that these methods all find more outbreaks when outbreaks are rare. This is encouraging, as early detection is critical for outbreak management. Overall, since the Spatial Proximity and Network Connectivity methods find a similar proportion of outbreaks, and are less data-intensive than the Network Proximity method, countries with endemic FMD whose resources are constrained could prioritize allocating sentinels based on whichever of those two methods requires less additional data collection.
Copyright: © 2025 Greiner et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Veterinary Services UA. Foot-and-mouth disease response plan: The red book. 2020.
-
- James AD, Rushton J. The economics of foot and mouth disease. Revue scientifique et technique (International Office of Epizootics). 2003;21:637–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

