Structural and genetic determinants of zebrafish functional brain networks
- PMID: 40644546
- PMCID: PMC12248300
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv7576
Structural and genetic determinants of zebrafish functional brain networks
Abstract
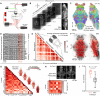
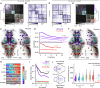
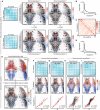
Network science has revealed universal brain connectivity principles across species. However, several macroscopic network features established in human neuroimaging studies remain underexplored at cellular scales in small animal models. Here, we use whole-brain calcium imaging in larval zebrafish to investigate the structural and genetic basis of functional brain networks. Mesoscopic functional connectivity (FC) robustly captures the individuality of larvae and reflects structural connectivity (SC) derived from single-neuron reconstructions. Several connectome properties, including diffusion mechanisms and indirect pathways, predict interregional correlations. SC and FC share a hierarchical modular architecture, with structural modules shaping spontaneous and stimulus-driven activity patterns. Visual stimuli and tail monitoring reveal a functional gradient that coincides with sensorimotor functions. Last, regional expression levels of specific genes predict interregional FC. Our findings reproduce key mammalian brain network features, demonstrating larval zebrafish as a powerful model for studying large-scale network phenomena in a small and optically accessible vertebrate brain.
Figures




References
-
- Ryan T. J., Grant S. G., The origin and evolution of synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 701–712 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Van den Heuvel M. P., Bullmore E. T., Sporns O., Comparative connectomics. Trends Cognit. Sci. 20, 345–361 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Bullmore E., Sporns O., The economy of brain network organization. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 336–349 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

