Integrative analysis identifies IL-6/JUN/MMP-9 pathway destroyed blood-brain-barrier in autism mice via machine learning and bioinformatic analysis
- PMID: 40645949
- PMCID: PMC12254206
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03452-x
Integrative analysis identifies IL-6/JUN/MMP-9 pathway destroyed blood-brain-barrier in autism mice via machine learning and bioinformatic analysis
Abstract
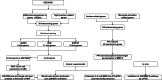
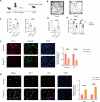
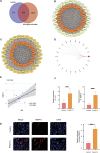
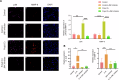
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by social communication deficits and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Growing evidence implicates neuroinflammation-induced blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction as a key pathogenic mechanism in ASD, although the underlying molecular pathways remain poorly understood. This study aimed to identify critical genes linking BBB function and neuroinflammatory activation, with the ultimate goal of evaluating potential therapeutic targets. Through integrative analysis combining differential gene expression profiling with three machine learning algorithms - Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression, Support Vector Machine Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE), and RandomForest combined with eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) - we identified four hub genes, with JUN emerging as a core regulator. JUN demonstrated strong associations with both BBB integrity and microglial activation in ASD pathogenesis. Using a maternal immune activation (MIA) mouse model of ASD, we observed significant downregulation of cortical tight junction proteins ZO-1 and occludin, confirmed through immunofluorescence and qPCR analysis. Bioinformatics analysis revealed a close correlation between JUN and IL-6/MMP-9 signaling in ASD-associated microglial activation. These findings were validated in vivo, with immunofluorescence and qPCR demonstrating elevated IL-6 and MMP-9 expression in ASD mice. Pharmacological intervention using ventricular JNK inhibitor administration effectively downregulated JUN and MMP-9 expression. In vitro studies using IL-6-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells replicated these findings, showing JNK inhibitor-mediated suppression of JUN and MMP-9 upregulation. These results collectively identify the IL-6/JUN/MMP-9 pathway as a specific mediator of barrier dysfunction in ASD, representing a promising target for personalized therapeutic interventions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: This research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments conducted in this study were performed in strict compliance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Approval No. 4025).
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on expression in blood-brain barrier in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating HIF-1α/VEGF/MMP-9 signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jun 25;50(6):613-623. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20241047. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40551643 Chinese.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and mechanisms for keloid disorder based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and machine learning algorithms.BMC Med Genomics. 2025 Jul 1;18(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12920-025-02174-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40598145 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11(11):CD011144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29159857 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Shared Gene Signatures and Immune Infiltration Characteristics Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning.Reprod Sci. 2025 Jun;32(6):1886-1904. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01847-1. Epub 2025 May 15. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40374866
-
Gut microbiota and behavioral ontogeny in autism spectrum disorder: a pathway to therapeutic innovations.Physiol Behav. 2025 Oct 1;299:114989. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2025.114989. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Physiol Behav. 2025. PMID: 40505847 Review.
References
-
- Maenner MJ, Warren Z, Williams AR, Amoakohene E, Bakian AV, Bilder DA, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2023;72:1–14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yin H, Wang Z, Liu J, Li Y, Liu L, Huang P, et al. Dysregulation of immune and metabolism pathways in maternal immune activation induces an increased risk of autism spectrum disorders. Life Sci. 2023;324:121734. - PubMed
-
- Hughes HK, Moreno RJ, Ashwood P. Innate immune dysfunction and neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Brain Behav Immun. 2023;108:245–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

