Chromosome-level genome assembly with telomeric repeats at scaffold ends for Rhabdosargus sarba
- PMID: 40645974
- PMCID: PMC12254218
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05324-x
Chromosome-level genome assembly with telomeric repeats at scaffold ends for Rhabdosargus sarba
Abstract
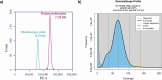
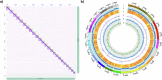
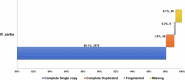
Rhabdosargus sarba, the goldlined seabream, is a euryhaline marine fish of great aquaculture potential. Genome sequencing and assembly of R. sarba was carried utilizing a multi-platform sequencing strategy that included long-read sequencing (PacBio HiFi), short-read sequencing (Illumina), and chromatin interaction mapping (Hi-C). The final genome assembly size after scaffolding was 764.59 Mb in 31 scaffolds with an N50 length of 33.98 Mb. Repeat profiling of primary assembly showed that 28.71% of the genome comprises of repeat elements. Gene prediction utilising the evidence from ab initio prediction and transcriptome data revealed 26,913 protein encoding genes and functional annotation and pathway analysis showed their participation in 332 pathways. This genome is an excellent resource for future research on genetic improvement and molecular breeding programmes for R. sarba.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Jiang ShiGui, J. S., Liu HongYan, L. H., Su TianFeng, S. T. & Gong ShiYuan, G. S. Molecular phylogeny of mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences from four Sparidae fishes. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China10, 184–188 (2003).
-
- Li, J. et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Rhabdosargus sarba (Perciformes: Sparidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A27, 1606–1607 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

