Cross-population GWAS and proteomics improve risk prediction and reveal mechanisms in atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 40645996
- PMCID: PMC12254421
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61720-2
Cross-population GWAS and proteomics improve risk prediction and reveal mechanisms in atrial fibrillation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Cross-population GWAS and proteomics improve risk prediction and reveal mechanisms in atrial fibrillation.Nat Commun. 2025 Oct 3;16(1):8811. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-64765-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 41044100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
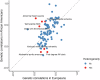
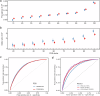
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common cardiac arrhythmia with strong genetic components, yet its underlying molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets remain incompletely understood. We conducted a cross-population genome-wide meta-analysis of 168,007 AF cases and identified 525 loci that met genome-wide significance. Two loci of PITX2 and ZFHX3 genes were identified as shared across populations of different ancestries. Comprehensive gene prioritization approaches reinforced the role of muscle development and heart contraction while also uncovering additional pathways, including cellular response to transforming growth factor-beta. Population-specific genetic correlations uncovered common and unique circulatory comorbidities between Europeans and Africans. Mendelian randomization identified modifiable risk factors and circulating proteins, informing disease prevention and drug development. Integrating genomic data from this cross-population genome-wide meta-analysis with proteomic profiling significantly enhanced AF risk prediction. This study advances our understanding of the genetic etiology of AF while also enhancing risk prediction, prevention strategies, and therapeutic development.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.M.D. receives research support from RenalytixAI and in-kind research support from Novo Nordisk, both outside the scope of the current project. D.G. is the Chief Executive Officer of Sequoia Genetics, a private limited company that works with investors, pharma, biotech, and academia by performing research that leverages genetic data to help inform drug discovery and development. D.G. has financial interests in several biotechnology companies. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Joseph, P. G. et al. Global variations in the prevalence, treatment, and impact of atrial fibrillation in a multi-national cohort of 153 152 middle-aged individuals. Cardiovasc. Res.117, 1523–1531 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Low, S. K. et al. Identification of six new genetic loci associated with atrial fibrillation in the Japanese population. Nat. Genet.49, 953–958 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

