Developmental transcriptomics reveals stage-specific immune gene expression profiles in Spodoptera frugiperda
- PMID: 40646005
- PMCID: PMC12254264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06939-1
Developmental transcriptomics reveals stage-specific immune gene expression profiles in Spodoptera frugiperda
Abstract
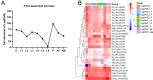
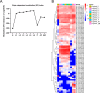
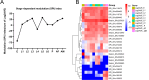
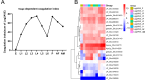
The fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, a globally invasive pest, demonstrates distinct immune adaptations across developmental stages and sexes, which are critical for its survival and adaptability. Using high-throughput RNA sequencing, this study systematically profiled 56 immune-related gene families, identifying 157 genes involved in Toll and Imd signaling pathways, and 185 genes associated with cellular immunity. Dynamic expression patterns were observed, with humoral immunity indices peaking during the third (L3) and fifth (L5) instars and diminishing in the pupal (P) and egg stages. In contrast, cellular immunity indices were highest in pupae and adult females, while the sixth instar (L6) and adult males exhibited the lowest immune capacity. Female adults displayed superior immune potential compared to males, reflecting evolutionary pressures tied to reproductive fitness. Notably, larval stages exhibited heightened immune gene expression, which aligns with their vulnerability to pathogens. Validation via qRT-PCR confirmed these transcriptomic trends, highlighting the modulation of immunity throughout development. These findings offer novel insights into the interplay between developmental progression and immune regulation in S. frugiperda. By elucidating these stage-specific immune responses, this study provides a robust framework for developing targeted pest management strategies aimed at mitigating the impact of this destructive pest.
Keywords: Spodoptera frugiperda; Cellular immunity; Development; Humoral immunity; Transcriptomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
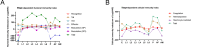






References
-
- Strand, M. R. The insect cellular immune response. Insect Sci.15, 1–14 (2008).
-
- Eleftherianos, I., Baldwin, H., ffrench-Constant, R. H. & Reynolds, S. E. Developmental modulation of immunity: changes within the feeding period of the fifth larval stage in the defence reactions of Manduca sexta to infection by Photorhabdus. J. Insect Physiol.54, 309–318 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

