Combination of machine learning and Raman spectroscopy for prediction of drug release in targeted drug delivery formulations
- PMID: 40646100
- PMCID: PMC12254238
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10417-z
Combination of machine learning and Raman spectroscopy for prediction of drug release in targeted drug delivery formulations
Abstract
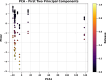
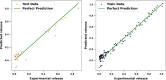
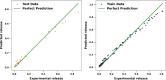
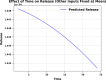
In this research, advanced regression techniques are investigated for modeling intricate release patterns utilizing a high-dimensional dataset comprising more than 1500 spectrum-based variables and categorical inputs. The spectral data are collected from Raman spectroscopy for analysis of drug release from a solid dosage formulation coated with Polysaccharides (a high-dimensional dataset of 155 samples, with drug release measured at 2, 8, and 24 h). The considered drug is 5-aminosalicylic acid for colonic drug delivery, and its release was estimated using Raman data as inputs along with other categorical parameters. The models, including Kernel Ridge Regression (KRR), Kernel-based Extreme Learning Machine (K-ELM), and Quantile Regression (QR) incorporate sophisticated approaches like the Sailfish Optimizer (SFO) for hyperparameter optimization and K-fold cross-validation to enhance predictive accuracy. Notably, KRR exhibited exceptional performance, achieving an R² of 0.997 on the training set and 0.992 on the test set, with a mean squared error (MSE) of 0.0004. In comparison, K-ELM and QR achieved lower R² values of 0.923 and 0.817 on the test set, respectively. The key innovation lies in integrating these non-linear regression models with robust data preprocessing steps, including dimensionality reduction via Principal Component Analysis (PCA), categorical feature encoding through Leave-One-Out (LOO), and outlier detection using Isolation Forest. This study significantly contributes by offering a comprehensive framework for managing high-dimensional and heterogeneous datasets, while emphasizing the effectiveness of optimization strategies in predictive modeling. By accurately predicting the release of 5-ASA from polysaccharide-coated formulations, these models can aid in the design of targeted colonic delivery formulations with optimized release kinetics, ultimately enhancing the efficacy of treatments for colonic diseases.
Keywords: Colonic drug delivery; Drug release; Kernel ridge regression; Kernel-based extreme learning machine; Quantile regression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Implementing partial least squares and machine learning regressive models for prediction of drug release in targeted drug delivery application.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22461. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06227-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594227 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Stabilizing machine learning for reproducible and explainable results: A novel validation approach to subject-specific insights.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025 Sep;269:108899. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2025.108899. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40570739
-
Oral budesonide for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 26;2015(10):CD007698. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007698.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497719 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches for predicting dairy cattle methane emissions: from traditional methods to machine learning.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae219. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae219. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39123286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adiguzel, S. et al. Doxorubicin-loaded liposome-like particles embedded in chitosan/hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels as a controlled drug release model for local treatment of glioblastoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.278, 135054 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Hu, J. et al. Modelling the controlled drug release of push-pull osmotic pump tablets using DEM. Int. J. Pharm.660, 124316 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Alqarni, M. et al. Model development using hybrid method for prediction of drug release from biomaterial matrix. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst.253, 105216 (2024).
-
- Biswas, A. A. et al. Development and comparison of machine learning models for in-vitro drug permeation prediction from microneedle patch. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.199, 114311 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Chaurawal, N. et al. Development of fucoidan/polyethyleneimine based sorafenib-loaded self-assembled nanoparticles with machine learning and DoE-ANN implementation: optimization, characterization, and in-vitro assessment for the anticancer drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.279, 135123 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

