TREM2-mediated regulation of microglial activity: a promising target for the treatment of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 40646506
- PMCID: PMC12247297
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06799-3
TREM2-mediated regulation of microglial activity: a promising target for the treatment of ischemic stroke
Abstract
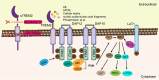
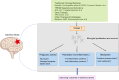
Ischemic stroke, the most prevalent type of stroke globally, poses significant challenges due to its high incidence, morbidity, and long-term disability. Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS), play a dual role in the context of ischemic stroke. While they contribute to neuroinflammation by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and exacerbating neuronal injury, they also facilitate tissue repair, angiogenesis, and restoration of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity through the secretion of anti-inflammatory and neurotrophic factors. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), predominantly expressed on microglia, is a critical regulator of microglial proliferation, survival, phagocytosis, polarization, inflammation, and metabolism. TREM2 has emerged as a key modulator of immune responses in ischemic stroke. This review provides a comprehensive examination of the multifaceted roles of TREM2 in microglial biology during ischemic stroke, integrating current insights into its molecular mechanisms. Furthermore, it highlights TREM2's potential as a transformative therapeutic target, advancing our understanding of neuroimmune regulation and promoting recovery after stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Therapeutic target; Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors have approved this manuscript for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Peisker T, Koznar B, Stetkarova I, et al. Acute stroke therapy: A review[J]. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017;27(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2018 update: A report from the American heart Association[J]. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67–492. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN. Role of macrophages/microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis[J]. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997;75(3):165–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

