RMDNet: RNA-aware dung beetle optimization-based multi-branch integration network for RNA-protein binding sites prediction
- PMID: 40646507
- PMCID: PMC12247420
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-025-06197-y
RMDNet: RNA-aware dung beetle optimization-based multi-branch integration network for RNA-protein binding sites prediction
Abstract
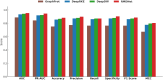
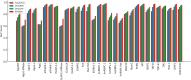
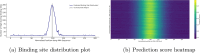
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play crucial roles in gene regulation. Their dysregulation has been increasingly linked to neurodegenerative diseases, liver cancer, and lung cancer. Although experimental methods like CLIP-seq accurately identify RNA-protein binding sites, they are time-consuming and costly. To address this, we propose RMDNet-a deep learning framework that integrates CNN, CNN-Transformer, and ResNet branches to capture features at multiple sequence scales. These features are fused with structural representations derived from RNA secondary structure graphs. The graphs are processed using a graph neural network with DiffPool. To optimize feature integration, we incorporate an improved dung beetle optimization algorithm, which adaptively assigns fusion weights during inference. Evaluations on the RBP-24 benchmark show that RMDNet outperforms state-of-the-art models including GraphProt, DeepRKE, and DeepDW across multiple metrics. On the RBP-31 dataset, it demonstrates strong generalization ability, while ablation studies on RBPsuite2.0 validate the contributions of individual modules. We assess biological interpretability by extracting candidate binding motifs from the first-layer CNN kernels. Several motifs closely match experimentally validated RBP motifs, confirming the model's capacity to learn biologically meaningful patterns. A downstream case study on YTHDF1 focuses on analyzing interpretable spatial binding patterns, using a large-scale prediction dataset and CLIP-seq peak alignment. The results confirm that the model captures localized binding signals and spatial consistency with experimental annotations. Overall, RMDNet is a robust and interpretable tool for predicting RNA-protein binding sites. It has broad potential in disease mechanism research and therapeutic target discovery. The source code is available https://github.com/cskyan/RMDNet .
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Dung beetle optimizer; Feature fusion strategy; Graph neural network; Multi-branch deep learning network; RNA–protein binding sites.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

