Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin attenuates memory impairments in diabetic rats
- PMID: 40646571
- PMCID: PMC12255018
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-025-01820-7
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin attenuates memory impairments in diabetic rats
Abstract
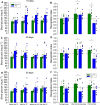
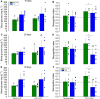
Cognitive decline is a significant complication of type 1 diabetes (T1D) that substantially affects patients' quality of life. Although previous studies suggest that Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin may mitigate certain effects of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes (T1DSTZ), the impact of NPH on diabetes-related cognitive decline remains unclear. This study evaluated the efficacy of NPH insulin in attenuating spatial, short-term, and long-term memory deficits in T1DSTZ rats, assessing their progression at 10, 20, and 30 days following diabetes induction and treatment initiation. Sixteen adult male Wistar rats were randomly assigned into diabetic and non-diabetic groups; T1D was induced using streptozotocin (STZ). Diabetic rats received twice-daily injections of NPH insulin and underwent cognitive assessments using the Novel Object Recognition and Spatial Object Recognition tasks. NPH insulin treatment delayed the progression of memory deficits in T1DSTZ rats over the 30-day period. Although memory function was not fully restored, insulin treatment effectively delayed deficits across spatial, short-term, and long-term memory domains. However, despite treatment, T1DSTZ rats still exhibited memory impairments, highlighting the complexity of diabetes-associated cognitive decline. These findings suggest that NPH insulin offers partial neuroprotection in T1DSTZ rats, underscoring the importance of early and consistent diabetes management to preserve cognitive function. Future research should focus on refining insulin therapy strategies to enhance their effectiveness in preventing and reducing diabetes-associated cognitive impairments.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Diabetes complications; Insulin therapy; Memory deficits; Neuroprotection; Streptozotocin-induced diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, Pavkov ME, Ramachandaran A, Wild SH, James S, Herman WH, Zhang P, Bommer C, Kuo S, Boyko EJ, Magliano DJ. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabet Res Clin Pract. 2022. 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Insel RA, Dunne JL, Atkinson MA, Chiang JL, Dabelea D, Gottlieb PA, Greenbaum CJ, Herold KC, Krischer JP, Lernmark A, Ratner RE, Rewers MJ, Schatz DA, Skyler JS, Sosenko JM, Ziegler AG. Staging presymptomatic type 1 diabetes: a scientific statement of jdrf, the endocrine society, and the American diabetes association. Diabetes Care. 2015. 10.2337/dc15-1419. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

