Orphan nuclear receptor transcription factors as drug targets
- PMID: 40646688
- PMCID: PMC12263127
- DOI: 10.1080/21541264.2025.2521766
Orphan nuclear receptor transcription factors as drug targets
Abstract
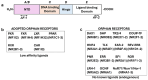
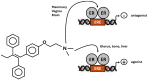
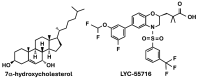
The nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily of ligand-activated receptors plays a key role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and in pathophysiology. NRs can be subdivided into functional activities structural similarity and the existence of endogenous ligands. Most NRs are classified as those that are adopted orphan or orphan receptors which have only possible ligands or no identified endogenous ligands, respectively. In this review, the activities of the complete orphan receptor sub-family of transcription factors have been reviewed with a focus on the effects of possible endogenous (biochemicals), natural product-derived and synthetic ligands. Despite their lack of a bona-fide ligand, the orphan receptors bind structurally diverse compounds that exhibit tissue-specific agonist, antagonist and inverse agonist activities with potential for future development as clinical therapeutics for the treatment of multiple diseases.
Keywords: Orphan nuclear receptors; ligands; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

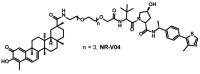

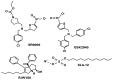
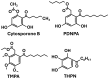
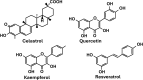
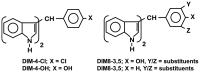
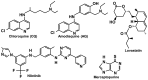
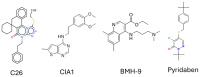
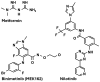
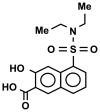
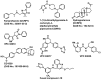
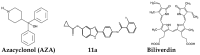
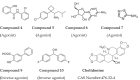
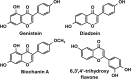
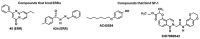
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
