Oxidative Stress Mediates the Dual Regulatory Effects of Bovine Uterine ECM Remodeling Through the TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathway: Molecular Mechanisms of MMPs and COL-IV Imbalances
- PMID: 40646747
- PMCID: PMC12248901
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15131847
Oxidative Stress Mediates the Dual Regulatory Effects of Bovine Uterine ECM Remodeling Through the TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathway: Molecular Mechanisms of MMPs and COL-IV Imbalances
Abstract
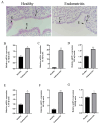
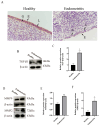
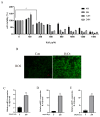
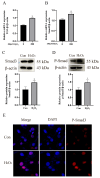
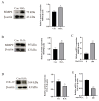
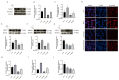
Bovine endometritis is a common endocrine and reproductive disorder in postpartum dairy cows, closely associated with elevated systemic oxidative stress. This disease can lead to delayed uterine involution, repeated breeding failure, and significant economic losses in the dairy industry. Studies suggest that oxidative stress may contribute to the pathological progression of endometritis by regulating ECM remodeling, but the specific molecular mechanisms remain unclear. ECM homeostasis relies on the coordinated action of matrix metalloproteinases (e.g., MMP2, MMP9) and collagen (e.g., type IV collagen, COL-IV), while the TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling pathway is implicated in ECM metabolic regulation. Therefore, elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of oxidative-stress-mediated TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling on ECM remodeling is crucial for understanding the pathogenesis of endometritis. This study investigates postpartum bovine uterine tissues, comparing inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and oxidative-stress-related factors (GPx, SOD, CAT) between healthy and endometritis groups. Additionally, the differences in ECM-remodeling-associated proteins (MMP2, MMP9, COL-IV) and TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway activity are analyzed. To further validate the mechanisms, an oxidative stress model is established in vitro by treating bovine endometrial epithelial cells (bEECs) with 200 μM H2O2 for 4 h, followed by the valuation of the same indicators. Furthermore, gene silencing to downregulate Smad3 expression or inhibitor-mediated suppression of TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway activity is performed to observe their regulatory effects on MMP2, MMP9, and COL-IV. The results demonstrate that oxidative-stress-mediated endometritis significantly upregulates MMP2, MMP9, and the TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway activity, while suppressing COL-IV expression. Functional genetic experiments further reveal the dual regulatory role of the TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway in ECM remodeling: (1) pathway activation promotes MMP2/MMP9 expression, accelerating COL-IV degradation; (2) Smad3 positively regulates COL-IV synthesis. These findings provide a theoretical basis for targeting the TGFβ1/Smad3 pathway to mitigate the pathological progression of endometritis.
Keywords: ECM remodeling; MMPs; TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway; bovine endometritis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCN5 negatively regulates TGF-β-induced endometriosis associated fibrosis through Wnt/β-catenin signaling via Smad3-dependent mechanism.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 10;23(1):763. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06804-9. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40640862 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of hydrogen peroxide-treated human chondrocytes shows endoplasmic reticulum stress, cytoskeleton remodeling, and altered secretome composition.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 13;23(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02291-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40514670 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The type I collagen paradox in PDAC progression: microenvironmental protector turned tumor accomplice.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 4;23(1):744. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06778-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40616159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu J., Feng X., Li B., Sun Y., Jin T., Feng M., Ni Y., Liu M. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GR-1 Alleviates Escherichia Coli-Induced Inflammation via NF-ΚB and MAPKs Signaling in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022;12:809674. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.809674. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Getahun A.M., Hunderra G.C., Gebrezihar T.G., Boru B.G., Desta N.T., Ayana T.D. Comparative Study on Lesions of Reproductive Disorders of Cows and Female Dromedary Camels Slaughtered at Addis Ababa, Adama and Akaki Abattoirs with Bacterial Isolation and Characterization. BMC Vet. Res. 2021;17:134. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02822-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

