Selenium-Biofortified Alfalfa Hay Supplemented to Jersey and Holstein Dairy Heifers During the Peripartum Period: Effects on Dams and Their Offspring
- PMID: 40646768
- PMCID: PMC12248524
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15131866
Selenium-Biofortified Alfalfa Hay Supplemented to Jersey and Holstein Dairy Heifers During the Peripartum Period: Effects on Dams and Their Offspring
Abstract
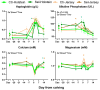
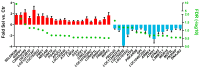
The objective of the study was to assess whether supplementing dairy heifers with Se-biofortified hay during the last 40 days of pregnancy and early lactation improves performance, metabolism, oxidative status, and immune response in the dams and their calves. Ten Jersey and eight Holstein pregnant dairy heifers were divided into two groups and supplemented with Se-biofortified or a control alfalfa hay from 40 days before to 2 weeks postpartum. The calves born to the heifers were also monitored during the first month of life. Supplementation of Se-biofortified hay improved milk yield in Holstein heifers only, but had minor effects on blood parameters measured and the liver transcriptome. Similarly, we did not detect any impact of feeding Se-biofortified hay to heifers on their offspring. The data indicated a better immune system and oxidative status in Holstein compared to Jersey heifers. Overall, our data did not support the hypothesis that supplementing Se-biofortified hay to pregnant heifers improves their performance and the health of dams and offspring, at least at the dose we provided.
Keywords: calves; immune status; oxidative stress; peripartum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigating the relationship between dairy dam preconception and gestation characteristics and heifer offspring variables from birth to lactation.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Jul;108(7):7758-7774. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-26138. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 40306426
-
Effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation to first-calf beef heifers during late gestation on offspring physiology and performance.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf091. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf091. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40126062
-
Replacing sulfate with hydroxychloride sources of trace minerals modulated the growth performance and plasma indicators of inflammation and energy metabolism in beef heifers during periods of feed restriction and adaptation to a high-starch diet.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae362. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae362. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39607694
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

