Dietary Supplementation with Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Enhances Resistance to Aeromonas veronii Infection in Red Claw Crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus)
- PMID: 40646810
- PMCID: PMC12249474
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15131912
Dietary Supplementation with Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Enhances Resistance to Aeromonas veronii Infection in Red Claw Crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus)
Abstract
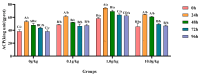
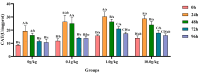
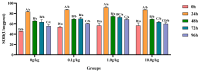
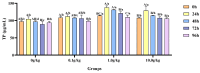
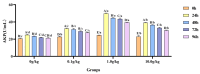
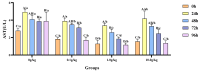
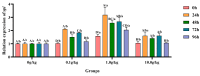
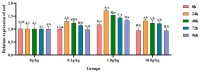
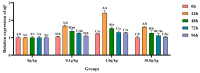
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of dietary supplementation with different levels of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa (0.0 g/kg, 0.1 g/kg, 1.0 g/kg, and 10.0 g/kg) on resistance to Aeromonas veronii infection in red claw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) (initial body weight of 0.13 ± 0.06 g). The investigation combined a 56-day feeding trial with a subsequent 7-day infection challenge to assess cumulative mortality, immune and antioxidant enzyme activities, and the relative expression of immune-related genes. During the A. veronii infection test, the cumulative mortalities for the 0.1 g/kg, 1.0 g/kg, and 10.0 g/kg groups were 44.44%, 38.89%, and 38.89%, respectively, all significantly lower (p < 0.05) than that of the control group (58.33%). Compared with the control group, after infection with A. veronii, the activities of acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase in the hepatopancreas and alkaline phosphatase, lysozyme in the hemolymph of red claw crayfish in the 1.0 g/kg group significantly increased (p < 0.05). The activities of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase in the hemolymph of red claw crayfish in the 1.0 g/kg group significantly decreased (p < 0.05). The relative expression levels of serine protease inhibitor, crustacean hyperglycemic hormone, anti-lipopolysaccharide factor, and superoxide dismutase genes in the hepatopancreas of red claw crayfish in the 1.0 g/kg group were significantly upregulated (p < 0.05). In conclusion, R. mucilaginosa could significantly improve the antibacterial ability of red claw crayfish against A. veronii. In this experimental context, the ideal addition level of R. mucilaginosa is determined to be 1.0 g/kg.
Keywords: Aeromonas veronii; Cherax quadricarinatus; Rhodotorula mucilaginosa; antioxidant; immune.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- He L., Xie Y., Lu W., Wang Y., Chen L., Mather P.B., Zhao Y., Wang Y., Wang Q. Genetic Diversity in Three Redclaw Crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus, von Martens) Lines Developed in Culture in China. Aquac. Res. 2012;43:75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2011.02802.x. - DOI
-
- El-Saadony M.T., Swelum A.A., Abo Ghanima M.M., Shukry M., Omar A.A., Taha A.E., Salem H.M., El-Tahan A.M., El-Tarabily K.A., Abd El-Hack M.E. Shrimp Production, the Most Important Diseases That Threaten It, and the Role of Probiotics in Confronting These Diseases: A Review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022;144:126–140. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.01.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y., Yu M., Liu J., Qiao Y., Wang L., Li Z., Zhang X., Yu M. Bacterial Community Associated with Healthy and Diseased Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Larvae and Rearing Water across Different Growth Stages. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:1362. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo L., Zhou M., Chen D., Yi C., Sun B., Wang S., Ru Y., Chen H., Wang H. A New Insight to Characterize Immunomodulation Based on Hepatopancreatic Transcriptome and Humoral Immune Factor Analysis of the Cherax quadricarinatus Infected with Aeromonas veronii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021;219:112347. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112347. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

