Odontogenic Abscesses in Pet Rabbits: A Comprehensive Review of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Advances
- PMID: 40646893
- PMCID: PMC12249203
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15131994
Odontogenic Abscesses in Pet Rabbits: A Comprehensive Review of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Advances
Abstract
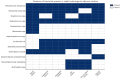
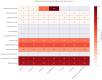
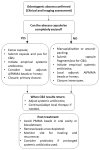
Odontogenic abscesses are a frequent and challenging clinical issue in pet rabbits, often requiring a comprehensive diagnostic and therapeutic approach. This review collates current evidence on the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of rabbit odontogenic abscesses, with a focus on imaging advances, microbial diversity, and local antimicrobial therapies. Predisposing factors include congenital conformation, inappropriate diet (insufficient abrasiveness, calcium or Vit D deficiencies, etc.), trauma, and neoplasia. Imaging techniques such as CT and cone-beam CT (CBCT) enable early detection and surgical planning, while traditional radiography remains useful in general practice. Treatment includes systemic antibiotics, surgical curettage, and the use of localized delivery systems such as antibiotic-impregnated polymethyl methacrylate (AIPMMA) beads. Adjunctive therapies like Manuka honey are also discussed. Two original heatmaps summarize bacterial prevalence and antimicrobial resistance from six peer-reviewed studies. These visualizations highlight the polymicrobial nature of these infections and the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains. Preventive strategies focus on optimal diet, regular dental checks, and owner education. The review also identifies key gaps in the literature, including the underreporting of anaerobes and lack of standardized treatment protocols. This article aims to support veterinary professionals in delivering evidence-based, individualized care to improve outcomes in rabbits with odontogenic abscesses.
Keywords: exotic animal medicine; odontogenic abscess; polymethyl methacrylate beads; rabbit dentistry; rabbit oral anatomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- DeMello M. Companion Animals in Everyday Life: Situating Human-Animal Engagement within Cultures. Palgrave Macmillan; London, UK: 2016. Rabbits Multiplying like Rabbits: The Rise in the Worldwide Popularity of Rabbits as Pets; pp. 91–107.
-
- Dobos P., Kulik L., Pongrácz P. The Amicable Rabbit—Interactions between Pet Rabbits and Their Caregivers Based on a Questionnaire Survey. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2023;260:105869. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2023.105869. - DOI
-
- Přibylová L., Součková M., Kolářová M.F., Vostrá-Vydrová H., Chaloupková H. Does a Stronger Bond with Pet Rabbits Equate to Better Husbandry Conditions for Them? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2024;270:106143. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2023.106143. - DOI
-
- Druce K. Dental Disease in Rabbits—Malocclusion. Vet. Nurs. J. 2015;30:309–311. doi: 10.1080/17415349.2015.1083922. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

