Corn Steep Liquor as an Efficient Bioresource for Functional Components Production by Biotransformation Technology
- PMID: 40646908
- PMCID: PMC12248704
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14132158
Corn Steep Liquor as an Efficient Bioresource for Functional Components Production by Biotransformation Technology
Abstract
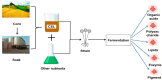
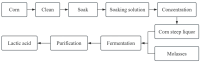
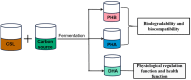
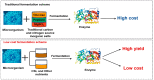
Corn is an important crop that can be used to produce many bioactive compounds. These functional components have been widely applied in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. Corn steep liquor (CSL) is a by-product of deep processing of corn that contains a lot of protein, peptides, amino acids, vitamins, and other nutrients, which is considered to be a rich and cheap source of plant nutrients. However, CSL is not widely used and factories are required to treat CSL as waste water directly; therefore, the question of how to turn CSL waste into a valuable product is likely to become a hot topic. In order to fully explore the potential utilization value of CSL, this review comprehensively summarizes the structural composition and nutritional characteristics of CSL, and its application and prospect in the biotransformation of industrialized organic acids, polysaccharides, lipids, enzymes, natural pigments, and novel functional components through the microbial fermentation pathway. Furthermore, specific methods for bioconverting various active substances using CSL were proposed, and the influences of various production conditions on the yield of the bioactive substances were fully analyzed and discussed. This article provides a reference for the efficient utilization of corn steep liquor as a by-product of corn processing.
Keywords: biotransformation; corn steep liquor; functional components; low cost; plant nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated devices for identifying peripheral arterial disease in people with leg ulceration: an evidence synthesis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Aug;28(37):1-158. doi: 10.3310/TWCG3912. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39186036 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Riccetto S., Davis A.S., Guan K., Pittelkow C.M. Integrated assessment of crop production and resource use efficiency indicators for the U.S. Corn Belt. Glob. Food Secur.-Agric. 2020;24:100339. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2019.100339. - DOI
-
- Cornejo M.W.d.l.Á., Rincón N., Del Real A., Rodríguez M.E. The effect of Ca2+ ions on the pasting, morphological, structural, vibrational, and mechanical properties of corn starch–water system. J. Cereal Sci. 2018;79:174–182. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2017.10.003. - DOI
-
- Liu H., Su B.B., Guo M., Wang J.B. Exploring R&D network resilience under risk propagation: An organizational learning perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024;273:109266.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

