Effects of Different Highland Barley Varieties on Quality and Digestibility of Noodles
- PMID: 40646914
- PMCID: PMC12248821
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14132163
Effects of Different Highland Barley Varieties on Quality and Digestibility of Noodles
Abstract
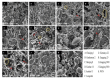
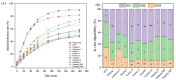
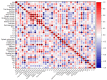
This study comprehensively assessed the effects of ten highland barley varieties on the quality and digestibility of noodles. The characteristics of highland barley flour, including proximate composition, pasting properties, and dough mixing behavior, were analyzed. The quality of the resulting noodles was evaluated through cooking and textural property analysis. The digestion characteristics of the noodles were determined to evaluate the starch hydrolysis rate and glycemic index (GI). Additionally, a correlation analysis was conducted among the proximate composition of highland barley flour, the characteristics of flour, and the quality of noodles. The results demonstrate that Chaiqing 1 exhibited superior performance in terms of flour quality and noodle texture compared to other varieties. The noodles produced from this variety possessed an outstanding texture, with moderate hardness and excellent elasticity. Additionally, its noodles also exhibited superior cooking resistance and low cooking loss. Nutritionally, the moderate estimated glycemic index (eGI) and high resistant starch (RS) content of Chaiqing 1 were beneficial for intestinal health. Ximalaya 22 showed good processing performance but slightly inferior texture, whereas Kunlun 14 had a high dietary fiber content, which resulted in noodles prone to breaking. Through a comprehensive variety comparison and screening, Chaiqing 1 emerged as the preferred choice for producing high-quality highland barley noodles. Furthermore, correlation analysis revealed that dietary fiber was significantly and positively correlated with water absorption, stability time (ST), and hardness (p < 0.01). Amylose content was associated with peak temperature and breakdown viscosity. This study provides valuable insights into the selection of highland barley varieties for noodle production.
Keywords: digestive characteristics; highland barley varieties; noodle quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Physicochemical Characterization of Wheat Flour Dough and Digestibility of White Salt Noodles With Different Resting Temperatures.J Food Sci. 2025 Jun;90(6):e70330. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70330. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40551615
-
Improved cooking quality and reduced in vitro digestibility in germinated highland barley noodles through synergistic modification with guar gum and Na2CO3.Food Res Int. 2025 Oct;218:116920. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116920. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40790640
-
Effects of replacing sucrose and blending extrusion modified flours on the eating quality of highland barley sugar-crisp cookies.Food Res Int. 2025 Oct;217:116818. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.116818. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40597528
-
Unveiling the Impact of Processing Methods on In Vitro Protein Digestibility: A Focus on Highland Barley and Its Application in Wine Production.Foods. 2025 Jun 7;14(12):2020. doi: 10.3390/foods14122020. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40565629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y., Wang Y., Liu H., Liu X. Effects of different crop starches on the cooking quality of Chinese dried noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022;57:2080–2092. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15488. - DOI
-
- Xi H., Wang A., Qin W., Nie M., Chen Z., He Y., Wang L., Liu L., Huang Y., Wang F., et al. The structural and functional properties of dietary fibre extracts obtained from highland barley bran through different steam explosion-assisted treatments. Food Chem. 2023;406:135025. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guo H., Lin S., Lu M., Gong J.D.B., Wang L., Zhang Q., Lin D., Qin W., Wu D. Characterization, in vitro binding properties, and inhibitory activity on pancreatic lipase of β-glucans from different Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley) cultivars. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018;120:2517–2522. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.023. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

