Supraclavicular Lymph Node Dissection in Breast Cancer with Synchronous Supraclavicular Metastases: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40647382
- PMCID: PMC12248947
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132081
Supraclavicular Lymph Node Dissection in Breast Cancer with Synchronous Supraclavicular Metastases: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background/objectives: Synchronous ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastases (sISLMs) in breast cancer are rare and associated with poor prognosis. The optimal locoregional treatment strategy remains unclear, particularly regarding the role of supraclavicular lymph node dissection (SLND).
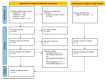
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis, including studies published up to end December 2023, to compare the outcomes of SLND combined with radiotherapy (RT) and systemic therapy (ST), SLND with ST alone, and ST alone, using RT + ST as the reference.
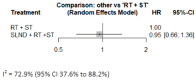
Results: Ten studies involving 3346 patients were included for overall survival (OS) analysis, and six studies were included for disease-free survival (DFS). SLND + RT + ST showed similar OS and DFS compared to RT + ST. Sensitivity analyses revealed that SLND limited to level V improved OS (HR: 0.47, 95% CI: 0.29-0.77), while more extensive dissections (level V+) worsened outcomes (HR: 1.41, 95% CI: 1.10-1.80).
Conclusions: These findings suggest that selective SLND may benefit certain patients, but broader application should be approached with caution pending results from future randomized trials.
Keywords: breast cancer; disease-free survival; locoregional therapy; network meta-analysis; overall survival; supraclavicular lymph node dissection; supraclavicular lymph node metastases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
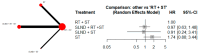
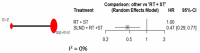
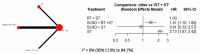

Similar articles
-
Axillary treatment for operable primary breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 4;1(1):CD004561. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004561.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28052186 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy for children with medulloblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 1;1(1):CD006678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25879092 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for the treatment of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers: surgical treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 31;8(8):CD006205. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006205.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37650478 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) for the preoperative locoregional staging of primary gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 6;2015(2):CD009944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009944.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25914908 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Arzanova E., Mayrovitz H.N. The Epidemiology of Breast Cancer. In: Mayrovitz H.N., editor. Breast Cancer. Exon Publications; Brisbane, Australia: 2022. - PubMed
-
- Pan H., Wang H., Qian M., Mao X., Shi G., Ma G., Yu M., Xie H., Ling L., Ding Q., et al. Comparison of Survival Outcomes Among Patients With Breast Cancer With Distant vs Ipsilateral Supraclavicular Lymph Node Metastases. JAMA Netw. Open. 2021;4:e211809. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1809. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brito R.A., Valero V., Buzdar A.U., Booser D.J., Ames F., Strom E., Ross M., Theriault R.L., Frye D., Kau S.W., et al. Long-term results of combined-modality therapy for locally advanced breast cancer with ipsilateral supraclavicular metastases: The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001;19:628–633. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.3.628. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

