Penile Cancer Profile in a Central European Context: Clinical Characteristics, Prognosis, and Outcomes-Insights from a Polish Tertiary Medical Center
- PMID: 40647438
- PMCID: PMC12248994
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132140
Penile Cancer Profile in a Central European Context: Clinical Characteristics, Prognosis, and Outcomes-Insights from a Polish Tertiary Medical Center
Abstract
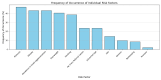
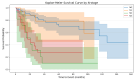
Background: Penile cancer is an uncommon malignancy in European and North America countries, accounting for less than 1% of malignant neoplasms. The etiology of penile cancer involves a complex interplay of clinical and behavioral factors, including phimosis, smoking, excess body weight, and HPV infection. The significance of these factors varies according to geographical and socioeconomic contexts. A comprehensive understanding of these interactions is essential for developing targeted prevention strategies and improving outcomes across diverse populations. However, the majority of existing studies originate from South America or Africa; there is a lack of data regarding these associations and prognoses in European populations, particularly in Central Europe, including Poland. Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of well-established clinical and behavioral characteristics associated with penile cancer and their influence on penile cancer prognosis in a cohort of 153 patients who underwent surgical intervention at a single tertiary medical center in Central Europe. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study was conducted from October 2011 to October 2024 at a single tertiary medical center and included 153 patients who underwent surgical treatment for penile cancer during this period. Demographic and histopathological data were collected. A comprehensive, self-administered patient survey was conducted to identify the presence of potentially relevant clinical and lifestyle characteristics. Moreover, the prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in penile cancer specimens was determined using p16 immunohistochemistry. Results: The median age of the participants in the study was 64 years (range: 30-87). The predominant identified features were phimosis (47.06%), residence in small agglomerations (43.14%), obesity (43.14%), overweight (40.52%), and smoking (38.56%). HPV infection was detected in only 14.38% of the patients. Phimosis was associated with a more locally advanced penile cancer stage (T-stage). The stage of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and histopathological grading significantly affected patient survival, with a poorer prognosis observed in more advanced stages and associated with poorly differentiated histopathological features. Among all the examined clinical and lifestyle characteristics, only smoking demonstrated a significant two-fold higher risk of mortality and was associated with a significantly lower overall survival compared to the absence of smoking (p = 0.047). Conversely, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection was associated with a six-fold reduction in the risk of death (p = 0.063). Conclusions: Phimosis was the most frequently observed clinical characteristic in our cohort study and was correlated with a more advanced penile cancer tumor stage. Smoking was associated with lower rates of patient survival, while HPV-positive patients demonstrated a trend toward lower mortality compared to HPV-negative patients.
Keywords: HPV; obesity; overweight; penile cancer; phimosis; prognosis; smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Coelho R.W.P., Pinho J.D., Moreno J.S., Garbis D.V.e.O., do Nascimento A.M.T., Larges J.S., Calixto J.R.R., Ramalho L.N.Z., da Silva A.A.M., Nogueira L.R., et al. Penile Cancer in Maranhão, Northeast Brazil: The Highest Incidence Globally? BMC Urol. 2018;18:50. doi: 10.1186/s12894-018-0365-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Strona Główna|Krajowy Rejestr Nowotworów. [(accessed on 15 May 2025)]. Available online: http://onkologia.org.pl/pl.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

