De Novo Renal Cell Carcinoma in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Incidence, Outcomes, and Therapeutic Challenges
- PMID: 40647498
- PMCID: PMC12248758
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132200
De Novo Renal Cell Carcinoma in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Incidence, Outcomes, and Therapeutic Challenges
Abstract
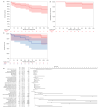
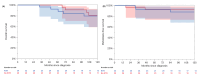
Background/Objectives: Kidney transplantation is associated with an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). This study aimed to evaluate the outcomes of de novo RCC in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs). Methods: We retrospectively identified 50 de novo RCC cases among 4012 KTRs transplanted from 2005 to 2024. Data on patient characteristics and outcomes were collected. Propensity score matching (PSM) compared 34 localized RCC cases in KTRs with 34 non-transplant RCC cases. The statistical analyses used Kaplan-Meier estimates, the log-rank test, and the Cox regression. Results: The RCC incidence was 0.64 per 1000 person-years, with a standardized incidence ratio of 4.40 (95% CI: 3.33-5.80). In the KTR cohort, clear cell RCC was present in 42%, and papillary RCC was present in 42%. RCC developed predominantly in native kidneys (92%). UICC stage I was present in 74%. The treatment for the non-metastatic RCC was nephrectomy in the majority of cases (91%). For the metastatic RCC, 71% received a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). In the KTR cohort, the 3- and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates were 85% and 72%, respectively, with a median OS of 199 months; the synchronous metastasized (M1) patients had a median OS of 14 months. Rejection, age, advanced UICC stage, higher pT stage, clinical positive lymph nodes, M1, and higher grade were significantly associated with poor OS. The 5-year OS (96% vs. 84%, p = 0.72) and MFS (92% vs. 93%, p = 0.61) were comparable in the PSM cohort between the KTRs and the non-KTRs in the localized RCC. Conclusions: KTRs have a higher risk of RCC and present at a localized stage with comparable OS rates to non-transplant RCC patients. Adverse tumor characteristics, including synchronous metastases, significantly affect the prognosis, highlighting the need for surveillance and individualized treatment, particularly for metastatic RCC.
Keywords: immunosuppressive therapy; kidney transplantation; oncological outcomes; propensity score matching; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
First-line therapy for adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 4;5(5):CD013798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37146227 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and gender as predictors for allograft and patient-relevant outcomes after kidney transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 19;12(12):CD014966. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014966.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39698949
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for induction therapy in kidney transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 11;1(1):CD004759. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004759.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28073178 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

