A Novel Treatment Strategy for Unresectable Locally Recurrent Rectal Cancer-Upfront Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy Followed by Surgical Resection of the Irradiated Intestines
- PMID: 40647528
- PMCID: PMC12249107
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132230
A Novel Treatment Strategy for Unresectable Locally Recurrent Rectal Cancer-Upfront Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy Followed by Surgical Resection of the Irradiated Intestines
Abstract
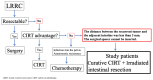
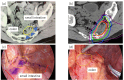
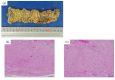
Background/Objectives: Carbon-ion radiotherapy (CIRT) is a promising treatment option for unresectable locally recurrent rectal cancer (LRRC). However, CIRT is contraindicated in cases where recurrent tumors are attached to the intestine. To address this limitation, we developed a novel treatment strategy involving curative-dose CIRT to recurrent tumors, including the adjacent intestine, without dose constraints, followed by surgical resection of the irradiated intestine. This study aimed to assess the feasibility of this approach. Methods: Patients were eligible for this study if the distance between the unresectable recurrent tumor and the adjacent intestines was less than 3 mm. Between 2019 and 2023, twelve patients were enrolled. CIRT was administered at curative doses of 70.4 or 73.6 Gy (relative biologic effectiveness (RBE)), including the adjacent intestines, without dose constraints. Surgical resection was not intended to excise the tumor itself, but was performed solely to remove the irradiated intestines. Irradiated intestine resection was planned within eight weeks after the completion of CIRT. Results: All patients completed the scheduled treatment course. The median interval between completing CIRT and surgery was 4 (3-8) weeks. No patients experienced acute AEs related to CIRT. Regarding late AEs, two patients developed Grade I sciatic neuralgia, and one patient developed Grade III neuralgia. We considered this symptom, which later resulted in a limp in his left leg, acceptable because this patient could ambulate with assistance. Clavien-Dindo Grade III postoperative complications occurred in one patient. The median follow-up duration was 40 (20-60) months. One patient was diagnosed with in-field recurrence, and three patients were diagnosed with out-of-field recurrence. These patients received reirradiation with CIRT. Four patients experienced lung recurrence, and one patient died from rectal-cancer-specific causes. Conclusions: This novel treatment strategy may provide favorable outcomes for patients with unresectable LRRC. This approach can be applied to the currently accepted indications for CIRT, and we believe that CIRT is a feasible treatment option for future patients.
Keywords: carbon-ion radiotherapy; locally recurrent rectal cancer; rectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does Augmenting Irradiated Autografts With Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in Patients With Bone Loss From a Malignant Tumor Achieve Union, Function, and Complication Rate Comparably to Patients Without Bone Loss and Augmentation When Reconstructing Intercalary Resections in the Lower Extremity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003599. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40569278
-
Composite Reconstruction With Irradiated Autograft Plus Total Hip Replacement After Type II Pelvic Resections for Tumors Is Feasible but Fraught With Complications.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Oct 1;482(10):1825-1835. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003097. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38666740
-
Hysterectomy with radiotherapy or chemotherapy or both for women with locally advanced cervical cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 7;(4):CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub3. PMID: 25847525 Updated.
-
What Are the Recurrence Rates, Complications, and Functional Outcomes After Multiportal Arthroscopic Synovectomy for Patients With Knee Diffuse-type Tenosynovial Giant-cell Tumors?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Jul 1;482(7):1218-1229. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002934. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38153106 Free PMC article.
-
Medical and surgical interventions for the treatment of usual-type vulval intraepithelial neoplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 5;2016(1):CD011837. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011837.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26728940 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

