Role of Human Microbiome in Development and Management of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 40647535
- PMCID: PMC12249478
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132238
Role of Human Microbiome in Development and Management of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Despite decades of research, cancer remains a major global health problem [...].
Keywords: HNSCC; chemotherapy; head and neck; immunotherapy; microbiome; radiotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
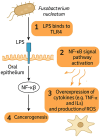
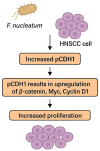

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

