Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells
- PMID: 40647536
- PMCID: PMC12248784
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132239
Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells
Abstract
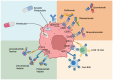
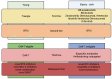
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare but heterogeneous subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) with a prognosis ranging from very favorable in indolent cases to a poor prognosis for more aggressive variants [...].
Keywords: bispecific antibodies; mantle cell lymphoma; monoclonal antibodies; post-CART; relapsed/refractory.
Conflict of interest statement
E.B.: honoraria from Astrazeneca, Amgen, Beigene, Mayo Clinic, travel grants from Kyowa Kirin. M.L.: reports consulting fees from Astrazeneca, Beigene, Janssen and Lilly. Honoraria for lectures, speaker’s bureaus or educational events from Astrazeneca, Beigene, Janssen and Lilly. Participation on data safety monitoring board with Acerta. C.A. speaker’s bureau and travel grant from Takeda. Honoraria for lectures from Taked and Novartis. A.C.: travel grant from Kyowa Kirin and Kite, spearker’s bureau from Roche and Kite. R.T.: honoraria from Lilly and Janssen. M.F.: honoraria from Astrazeneca, travel grant from Kite. M.M., L.C. and D.M. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 13;9(9):CD013365. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013365.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34515338 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Role of CAR-T Cell Therapy in the Context of Current Therapy Options for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma.Transplant Cell Ther. 2025 Jun 16:S2666-6367(25)01256-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2025.06.013. Online ahead of print. Transplant Cell Ther. 2025. PMID: 40516919 Review.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Epcoritamab Following Subcutaneous Administration in Relapsed or Refractory B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2025 Jan;64(1):127-141. doi: 10.1007/s40262-024-01464-2. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2025. PMID: 39708278 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II Study of Adaptive Manufactured Lentiviral Anti-CD20/Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Relapsed, Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jul 10;43(20):2285-2295. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02158. Epub 2025 Mar 31. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40163793 Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dreyling M., Campo E., Hermine O., Jerkeman M., Le Gouill S., Rule S., Shpilberg O., Walewski J., Ladetto M. Newly diagnosed and relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28((Suppl. 4)):iv62–iv71. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx223. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romaguera J.E., Medeiros L.J., Hagemeister F.B., Fayad L.E., Rodriguez M.A., Pro B., Younes A., McLaughlin P., Goy A., Sarris A.H., et al. Frequency of gastrointestinal involvement and its clinical significance in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer. 2003;97:586–591. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11096. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campo E., Jaffe E.S., Cook J.R., Quintanilla-Martinez L., Swerdlow S.H., Anderson K.C., Brousset P., Cerroni L., de Leval L., Dirnhofer S., et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood. 2022;140:1229–1253. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022015851. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

