Establishment of an Orthotopic and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Mouse Model Using a Tissue Adhesive-Based Implantation Method
- PMID: 40647563
- PMCID: PMC12249421
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17132266
Establishment of an Orthotopic and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Mouse Model Using a Tissue Adhesive-Based Implantation Method
Abstract
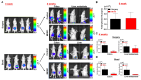
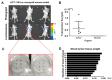
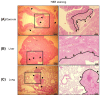
Background: To overcome the limitations of conventional CRC (colorectal cancer) mouse models in replicating metastasis and enabling efficient therapeutic evaluation, we developed a novel implantation method using tissue adhesive to establish reproducible orthotopic and metastatic tumors. Conventional models using injection or suturing techniques often suffer from technical complexity, inconsistent tumor establishment, and limited metastatic reliability. Methods: We developed and validated a novel orthotopic and metastatic CRC model utilizing tissue adhesive for tumor transplantation. Uniform tumor fragments derived from bioluminescent HCT116/Luc xenografts were affixed to the cecum of nude mice. Tumor growth and metastasis were monitored through bioluminescence imaging and confirmed by the results of histological analysis of metastatic lesions. The model's utility for therapeutic testing was evaluated using MK801, an NMDA receptor antagonist. Results: The biological-based model demonstrated rapid and reproducible tumor implantation (<5 min), consistent primary tumor growth, and robust metastasis to the liver and lungs. The biological-based approach achieved 80% tumor engraftment (4/5), with consistent metastasis to the liver and lungs in all mice, compared with lower and variable metastasis rates in injection (0%, 0/5) and suturing (20%, 1/5) methods. MK801 treatment significantly suppressed both primary tumor growth and metastasis, validating the model's suitability for preclinical drug evaluation. Conclusions: By enabling rapid, reproducible, and spontaneous formation of metastatic lesions using a minimally invasive tissue adhesive technique, our model represents a significant methodological advancement that supports high-throughput therapeutic screening and bridges the gap between experimental modeling and clinical relevance in colorectal cancer research.
Keywords: HCT116-Luc colon cancer cells; bioluminescence imaging; colorectal cancer; orthotopic model; preclinical drug evaluation; tissue adhesive (biological bond) implantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

