Evaluation of Maxillary Dentoalveolar Expansion with Clear Aligners: A Retrospective CBCT Study
- PMID: 40647585
- PMCID: PMC12248579
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15131586
Evaluation of Maxillary Dentoalveolar Expansion with Clear Aligners: A Retrospective CBCT Study
Abstract
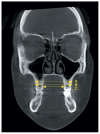
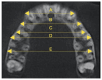
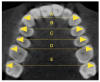
Background/Objectives: Currently, clear aligners are preferred to conventional appliances, especially among adult patients. However, the use of aligners for treating maxillary constriction is still debated in the literature. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to assess maxillary dentoalveolar expansion following clear aligner therapy in adults using CBCT scans. Methods: The study sample encompassed 50 non-growing patients (27 females and 23 males) aged 20 to 42 undergoing clear aligner orthodontics without dental extractions or auxiliaries. Transverse linear distances were measured on initial and final CBCTs and, subsequently, analysed through paired t-test and ANOVA. We considered alveolar bone measurements and interdental widths measured at the buccal apices and cusps from canines to second molars. Results: The buccal alveolar ridge width showed the greatest expansion (1.01 ± 0.38 mm), followed by the palatal alveolar ridge and maxillary alveolar bone. Statistically significant improvements were observed for all interdental measurements. The most considerable changes occurred in the interpremolar cusp distances, while the least changes were seen in the intermolar apex distances. At the cusp level, the average interpremolar widths increased by 3.44 ± 0.22 mm for the first premolars and 3.14 ± 0.27 mm for the second ones. Conclusions: Clear aligner treatment can effectively manage a constricted maxillary arch. We found significant changes in the maxillary alveolar bone. Both inter-apex and inter-cusp widths increased in all teeth, with the highest values in the premolars. Moreover, the increases in interdental distances at both apex and cusp levels were related to tooth position.
Keywords: 3D; CBCT; clear aligners; digital dentistry; maxillary expansion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Festa F., D’Anastasio R., Benazzi S., Macrì M. Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Maxillary Sinuses in Ancient Crania Dated to the V–VI Centuries BCE from Opi (Italy): Volumetric Measurements in Ancient Skulls from the Necropolis of Opi, Abruzzi, Italy. Diagnostics. 2024;14:1683. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151683. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

