Assessing the Accuracy of Diagnostic Capabilities of Large Language Models
- PMID: 40647657
- PMCID: PMC12248924
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15131657
Assessing the Accuracy of Diagnostic Capabilities of Large Language Models
Abstract
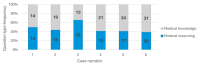
Background: In recent years, numerous artificial intelligence applications, especially generative large language models, have evolved in the medical field. This study conducted a structured comparative analysis of four leading generative large language models (LLMs)-ChatGPT-4o (OpenAI), Grok-3 (xAI), Gemini-2.0 Flash (Google), and DeepSeek-V3 (DeepSeek)-to evaluate their diagnostic performance in clinical case scenarios. Methods: We assessed medical knowledge recall and clinical reasoning capabilities through staged, progressively complex cases, with responses graded by expert raters using a 0-5 scale. Results: All models performed better on knowledge-based questions than on reasoning tasks, highlighting the ongoing limitations in contextual diagnostic synthesis. Overall, DeepSeek outperformed the other models, achieving significantly higher scores across all evaluation dimensions (p < 0.05), particularly in regards to medical reasoning tasks. Conclusions: While these findings support the feasibility of using LLMs for medical training and decision support, the study emphasizes the need for improved interpretability, prompt optimization, and rigorous benchmarking to ensure clinical reliability. This structured, comparative approach contributes to ongoing efforts to establish standardized evaluation frameworks for integrating LLMs into diagnostic workflows.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; diagnostic accuracy; large language modes; medical education.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Wang S., Ouyang Q., Wang B. Comparative Evaluation of Commercial Large Language Models on PromptBench: An English and Chinese Perspective. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint . - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

