The Physiological Mechanisms and Hurdles of Efficient Water-Nitrogen Utilization in Maize Production: A Review
- PMID: 40647908
- PMCID: PMC12252136
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14131899
The Physiological Mechanisms and Hurdles of Efficient Water-Nitrogen Utilization in Maize Production: A Review
Abstract
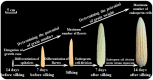
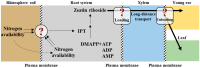
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most important staple food crops globally. One-third of global maize production is located in areas with high or extreme water scarcity and concurrently faces the challenge of low nitrogen use efficiency. Therefore, achieving synergistically high-efficiency water and nitrogen utilization in maize production is of great significance for agricultural sustainable development and global food security. In recent years, more articles have focused on the physiological mechanisms and management practices of efficient water and nitrogen utilization in maize. Unfortunately, there is a relative scarcity of research on the interactive effects between water and nitrogen on the development of young ears, which plays a crucial role in maize productivity. By compiling the most pertinent publications, this review endeavors to consolidate the existing knowledge on the interactive effects between water and nitrogen on maize production. Moreover, it advances potential physiological mechanisms and strategies for high-efficiency water and nitrogen utilization in terms of root system functioning, phytohormones, metabolism, and organ development. The changes in the availability of water and nitrogen have a significant impact on the development of young ears during the critical period, which in turn directly determines the grain number per ear and grain weight.
Keywords: cytokinin; deficit irrigation; ear development; floret primordium; maize; nitrogen; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Erenstein O., Jaleta M., Sonder K., Mottaleb K., Prasanna B.M. Global maize production, consumption and trade: Trends and R&D implications. Food Secur. 2022;14:1295–1319. doi: 10.1007/s12571-022-01288-7. - DOI
-
- Wang X., Tan W., Zhou S., Xu Y., Cui T., Gao H., Chen M., Dong X., Sun H., Yang J., et al. Converting maize production with low emergy cost and high economic return for sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;136:110443. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110443. - DOI
-
- National Bureau of Statistics. [(accessed on 15 May 2025)];2024 Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01.
-
- Li J., Xu X., Liu L., Deng X., Wang S. Impact of irrigation on cropland yield potential and scenario-based optimization in Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2025;314:109522. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2025.109522. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

