Effects of Seedling Substrate and Hydroponic Versus Aquaponic Nutrient Solution on Growth, Nutrient Uptake, and Eco-Physiological Response of Lemon Basil (Ocimum × citriodorum)
- PMID: 40647938
- PMCID: PMC12251977
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14131929
Effects of Seedling Substrate and Hydroponic Versus Aquaponic Nutrient Solution on Growth, Nutrient Uptake, and Eco-Physiological Response of Lemon Basil (Ocimum × citriodorum)
Abstract
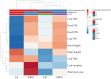
Lemon basil (Ocimum × citriodorum) is a highly valued aromatic plant renowned for its distinct citrus aroma. This study aimed to evaluate sustainable substrates and cultivation systems for its production. Two complementary and sequential experiments were conducted: an initial experiment designed to compare coconut fiber mixed in varying proportions with perlite to rock wool, evaluating their effectiveness during germination and early growth (experiment 1), and a subsequent experiment aimed at assessing plant performance in a decoupled aquaponic system relative to hydroponics utilizing the best-performing coconut fiber-perlite mixture from the first phase along with rock wool as substrates (experiment 2). The substrate with 70% coconut fiber and 30% perlite (F70:P30) significantly improved seed germination, leaf number, and total leaf area of seedlings. The decoupled aquaponic cultivation system resulted in a 52.5% increase in flavonoid content, accompanied by higher calcium and magnesium uptake in stems and roots compared to hydroponics. These findings clearly underscore the potential of coconut fiber substrates mixed with perlite as sustainable alternatives to rock wool, reducing environmental impact, disposal costs, and health risks. Similarly, aquaponic cultivation emerges as a valuable strategy for sustainable lemon basil (Ocimum × citriodorum) production, offering comparable yields to hydroponics while improving plant nutritional and phytochemical quality through beneficial plant-microbe interactions. These results provide practical evidence supporting the adoption of environmentally friendly substrates and cultivation practices, thus contributing significantly toward sustainable intensive vegetable production systems.
Keywords: aquaponics; coconut fiber; flavonoids; lemon basil (Ocimum × citriodorum); soilless cultivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Spence C. Sweet Basil: An Increasingly Popular Culinary Herb. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024;36:100927. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2024.100927. - DOI
-
- Boronat Ò., Mora M., Romeo-Arroyo E., Vázquez-Araújo L. Unraveling the Mediterranean Cuisine. What Ingredients Drive the Flavor of the Gastronomies Included in the Mediterranean Diet? Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023;34:100802. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2023.100802. - DOI
-
- Matarazzo N., Imbrenda V., Coluzzi R., Pace L., Samela C., Lanfredi M. ‘Industrializzazione Dell’ Agricoltura Nella Piana Del Sele: Una Prospettiva Geografica Basata Sull’ Urban Atlas Copernicus. Bull. Dell’assoc. Ital. Cartogr. 2022;175:101–113. doi: 10.13137/2282-572X/35443. - DOI
-
- Stolte J., Tesfai M., Øygarden L., Hessel R., Panagos P., Kværnø S., Verheijen F., Ballabio C., Stolte J., Keizer J. Soil Threats in Europe. Publications Office; Luxemburg: 2015. - DOI
Grants and funding
- Innovation in Cultivation Techniques for Leafy Vegetables to Reduce Environmental Impact through the Reduction of Chemical Fertilizers/Rago Group
- Code CN_00000033, CUP E63C22000990007/National Biodiversity Future Center - NBFC funded by the European Union - NextGenerationEU under the NRRP, Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.4.
- Project code: 2020ELWM82, CUP: J33C20002350001/Italian Ministry of Education and Research (MUR) within the call for Research Projects of National Interest (PRIN), within the project "VFARM-Sustainable Vertical Farming"
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

