MdGRF22, a 14-3-3 Family Gene in Apple, Negatively Regulates Drought Tolerance via Modulation of Antioxidant Activity and Interaction with MdSK
- PMID: 40647977
- PMCID: PMC12252163
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14131968
MdGRF22, a 14-3-3 Family Gene in Apple, Negatively Regulates Drought Tolerance via Modulation of Antioxidant Activity and Interaction with MdSK
Abstract
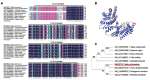
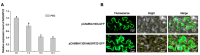
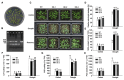
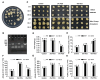
The 14-3-3 proteins play crucial roles in regulating plant growth, development, signal transduction and abiotic stress responses. However, there exists a scarcity of research on the role of 14-3-3 proteins in responding to abiotic stress in apples. In this study, we isolated the MdGRF22 gene from the apple 14-3-3 family. Through the screening of interacting proteins and genetic transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana and apple callus tissues, the function of the MdGRF22 gene under drought stress was verified. The coding sequence (CDS) of MdGRF22 consists of 786 bp and encodes for 261 amino acids. Through sequence alignment, the conserved 14-3-3 domain was identified in MdGRF22 and its homologous genes, which also share similar gene structures and conserved motifs. Subcellular localization revealed that the MdGRF22 protein was predominantly located in the cytoplasm and cell membrane. The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) analysis demonstrated a possible interaction between MdGRF22 and MdSK. In addition, MdGRF22 transgenic plants generally exhibited lower superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) activities, higher malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and relative electrolyte leakage under drought conditions compared with wild-type (WT) plants. Our study suggests that MdGRF22 may reduce the drought resistance of transgenic A. thaliana and callus tissues by interacting with MdSK. This study provides a theoretical basis for further exploring the function of 14-3-3 family genes.
Keywords: MdGRF22; Y2H; antioxidant system; apple.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

