Genome-Wide Characterization of the ANN Gene Family in Corydalis saxicola Bunting and the Role of CsANN1 in Dehydrocavidine Biosynthesis
- PMID: 40647984
- PMCID: PMC12252069
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14131974
Genome-Wide Characterization of the ANN Gene Family in Corydalis saxicola Bunting and the Role of CsANN1 in Dehydrocavidine Biosynthesis
Abstract
Annexins (ANNs) are a family of calcium (Ca2+)-dependent and phospholipid-binding proteins, which are implicated in the regulation of plant growth and development as well as protection from biotic and abiotic stresses. Corydalis saxicola Bunting, an endangered benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA)-rich herbaceous plant, widely used in traditional Chinese medicine, is endemic to the calciphilic karst region of China. However, whether and how ANNs are involved in the biosynthesis pathway of BIAs and/or help C. saxicola plants cope with abiotic properties, such as calcareous soils, are largely unknown. Here, nine CsANN genes were identified from C. saxicola, and they were divided into three subfamilies, namely subfamilies I, II, and IV, based on the phylogenetic tree. The CsANNs clustered into the same clade, sharing similar gene structures and conserved motifs. The nine CsANN genes were located on five chromosomes, and their expansions were mainly attributed to tandem and whole-genome duplications. The CsANN transcripts displayed organ-specific and Ca2+-responsive expression patterns across various tissues. In addition, transient overexpression assays showed that CsANN1 could positively regulate the accumulation of BIA compounds in C. saxicola leaves, probably by directly interacting with key BIA-biosynthetic-pathway enzymes or by interacting with BIA-biosynthetic regulatory factors, such as MYBs. This study sheds light on the profiles and functions of the CsANN gene family and paves the way for unraveling the molecular mechanism of BIA accumulation, which is regulated by Ca2+ through CsANNs.
Keywords: Corydalis saxicola Bunting; annexin; benzylisoquinoline alkaloid; calcium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
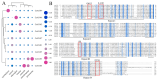





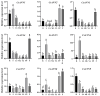



References
-
- Xu L., Chao T., Hua Z., Jin W., Fang W., Yi Y.M., Xi L., Hong Z., Chun Y., Bang C., et al. Investigation of the hepato-protective effect of Corydalis saxicola Bunting on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats by 1H-NMR-based metabonomics and network pharmacology approaches. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018;159:252–261. - PubMed
-
- Fan Z., Yang X., Zhen L., Xiao W., Dan H., Sui Z., Min L., De Y., Dong W., Yi W. Anti-hepatitis B virus effects of dehydrocheilanthifoline from Corydalis saxicola. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013;41:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Li C., Liu H., Qin M., Tan Y.J., Ou X.L., Chen X.Y., Wei Y., Zhang Z.J., Lei M. RNa editing events and expression profiles of mitochondrial protein-coding genes in the endemic and endangered medicinal plant, Corydalis saxicola. Front. Plant Sci. 2024;15:1332460. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1332460. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Guike AD22080016/the Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent Project
- 2025GXNSFBA069023; 2025GXNSFAA069814; 2023GXNSFAA026509/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi
- 32460105 and 32260107/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Guike AB23026092/Guangxi Key R&D Program
- GK ZY24212031/the Central Guidance on Local Science and Technology Development Fund of Guangxi
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

