Borohydride Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for SERS Platforms: Indirect Glucose Detection and Analysis Using Gradient Boosting
- PMID: 40648399
- PMCID: PMC12252442
- DOI: 10.3390/s25134143
Borohydride Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for SERS Platforms: Indirect Glucose Detection and Analysis Using Gradient Boosting
Abstract
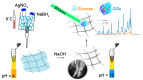
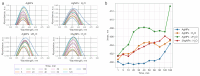
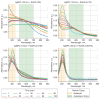
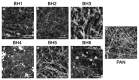
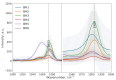
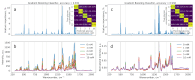
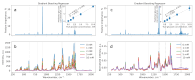
In recent years, non-invasive methods for the analysis of biological fluids have attracted growing interest. In this study, we propose a straightforward approach to fabricating silver nanoparticle (AgNP)-coated non-woven polyacrylonitrile substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). AgNPs were synthesized directly on the substrate using borohydride reduction, ensuring uniform distribution. The optimized SERS substrates exhibited a high enhancement factor (EF) of up to 105 for the detection of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA). To enable glucose sensing, the substrates were further functionalized with glucose oxidase (GOx), allowing detection in the 1-10 mM range. Machine learning classification and regression models based on gradient boosting were employed to analyze SERS spectra, enhancing the accuracy of quantitative predictions (R2 = 0.971, accuracy = 0.938, limit of detection = 0.66 mM). These results highlight the potential of AgNP-modified substrates for reliable and reusable biochemical sensing applications.
Keywords: SERS sensors; glucose detection; in situ AgNP synthesis; non-woven materials; polyacrylonitrile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

