The Six-Minute Walk Test in Community-Dwelling Older Adult Women: The Influence of Physical Activity Levels and Age-Related Factors
- PMID: 40648634
- PMCID: PMC12250147
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13131610
The Six-Minute Walk Test in Community-Dwelling Older Adult Women: The Influence of Physical Activity Levels and Age-Related Factors
Abstract
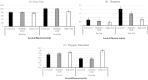
Background/Objectives: In the context of active ageing, functional assessment is key to preserving autonomy in older women. The six-minute walk test (6MWT) is a practical tool for estimating general health, but its results can be influenced by various factors. This study analysed cardiorespiratory variations during the 6MWT in older women according to their physical activity level and age-related variables such as pain, sarcopenia, frailty, and motivation to exercise. Methods: A total of 163 older women with musculoskeletal pain, but without cardiac or respiratory conditions, were classified into groups with high (HPA), moderate (MPA), and low (LPA) physical activity. During the 6MWT, heart rate (HR), dyspnoea, and oxygen saturation (SpO2) were recorded. Pain, sarcopenia, frailty, and motivation to exercise were also assessed. A repeated-measures multivariate analysis of (co)variance (RM-MANCOVA) was performed. Results: The results showed differences in HR depending on the level of physical activity, conditioned by sarcopenia (p < 0.05) and walked distance (p < 0.001), and in dyspnoea conditioned by pain perception (p < 0.01) and social (p < 0.001) and psychological (p < 0.05) motivation to exercise. There were also differences in SpO2 depending on the level of physical activity (p < 0.0001). There were differences between the HPA group and both the MPA and LPA group, which had higher HR, higher dyspnoea, and lower SpO2 when undergoing the 6MWT test. Conclusions: To accurately interpret 6MWT results in older adult women, it is essential to consider physical activity level, perceived pain, sarcopenia, and motivation to exercise, as these factors influence HR, dyspnoea, and SpO2. These variables should guide physical activity recommendations for healthy ageing.
Keywords: Six-Minute Walk Test; cardiorespiratory; older adults; physical activity; women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Valderrama F.P., Coronado F.B., Aichele C.V., Bravo E.C. Nivel de actividad física y funcionalidad en adultos mayores. Rev. Cienc. Act. Física UCM. 2016;17:59–65.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous