Assessing ChatGPT-v4 for Guideline-Concordant Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Accuracy, Completeness, and Temporal Drift
- PMID: 40648973
- PMCID: PMC12250039
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14134599
Assessing ChatGPT-v4 for Guideline-Concordant Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Accuracy, Completeness, and Temporal Drift
Abstract
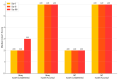
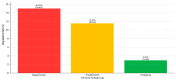
Background/Objectives: Chat Generative Pretrained Transformer (ChatGPT) is a useful resource for individuals working in the healthcare field. This paper will include descriptions of several ways in which ChatGPT-4 can achieve greater accuracy in its diagnosis and treatment plans for ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) by following the guidelines set out by the European Crohn's and Colitis Organization (ECCO). Methods: The survey, which comprised 102 questions, was developed to assess the precision and consistency of respondents' responses regarding the UC and CD. The questionnaire incorporated true/false and multiple-choice questions, with the objective of simulating real-life scenarios and adhering to the ECCO guidelines. We employed Likert scales to assess the responses. The inquiries were put to ChatGPT-4 on the initial day, the 15th day, and the 180th day. Results: The 51 true or false items demonstrated stability over a six-month period, with an initial accuracy of 92.8% at baseline, 92.8% on the 15th day, and peaked to 98.0% on the 180th day. This finding suggests a negligible effect size. The accuracy of the multiple-choice questions was initially 90.2% on Day 1, reached its highest point at 92.2% on Day 15, and then decreased to 84.3% on Day 180. However, the reliability of the data was found to be suboptimal, and the impact was deemed negligible. A modest, transient increase in performance was observed at 15 days, which subsequently diminished by 180 days, resulting in negligible effect sizes. Conclusions: ChatGPT-4 demonstrates potential as a clinical decision support system for UC and CD, but its assessment is marked by temporal variability and the inconsistent execution of various tasks. Essential initiatives that should be carried out before involving artificial intelligence (AI) technology in IBD trials are routine revalidation, multi-rater comparisons, prompt standardization, and the cultivation of a comprehensive understanding of the model's limitations.
Keywords: ChatGPT; artificial intelligence; clinical decision support; inflammatory bowel diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Burisch J., Vardi H., Pedersen N., Brinar M., Cukovic-Cavka S., Kaimakliotis I., Duricova D., Bortlik M., Shonová O., Vind I., et al. Costs and resource utilization for diagnosis and treatment during the initial year in a European inflammatory bowel disease inception cohort: An ECCO-EpiCom Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015;21:121–131. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000250. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sciberras M., Farrugia Y., Gordon H., Furfaro F., Allocca M., Torres J., Arebi N., Fiorino G., Iacucci M., Verstockt B., et al. Accuracy of Information given by ChatGPT for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Relation to ECCO Guidelines. J. Crohn’s Colitis. 2024;18:1215–1221. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae040. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

